Trigeminal Neuralgia: Causes, Diagnosis & Symptoms
M3 India Newsdesk May 27, 2024
Trigeminal neuralgia (TGN) is a persistent pain condition affecting the facial trigeminal nerve. This article explains the epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment of this condition.
Trigeminal Neuralgia (TGN)
The characteristic symptom of trigeminal neuralgia (TGN) is sudden, typically unilateral, recurring lancinating pain that originates from one or more trigeminal nerve divisions.
It is also known as, “Tic douloureux, prosopalgia, Suicide disease, Fothergill’s disease, Neuralgia epileptiforme”.
According to the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP), it is defined as a “Unilateral painful orofacial condition characterised by brief duration of electric shock-like sensation with an abrupt onset and termination, and limited to one or more sensory divisions of the trigeminal nerve”.
Epidemiology
- Age- 50-70 years
- Sex Predilection – Female (60%)
- Affliction for side: Predilection for the right side
- Multiple sclerosis – 1%
- Division of Nerve affected:
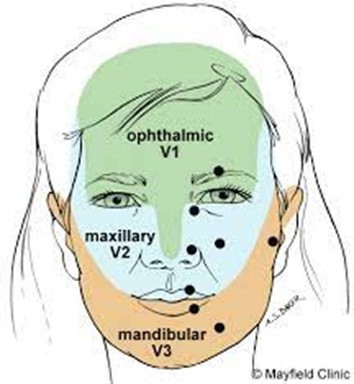
- Maxillary(V2)- 35%
- Mandibular (V3)- 29%
- Ophthalmic (V1)- 4%
- Maxillary & Mandibular- 19%
- All Branches- 1%
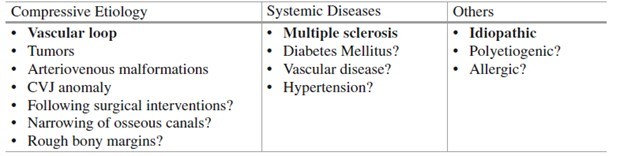
Aetiology
Diagnosis
When the following criteria are met in addition to at least three episodes of unilateral facial pain, TGN can be diagnosed;
- Pain occurring in one or more divisions of the trigeminal nerve, with no radiation beyond the trigeminal distribution
- Pain with at least three of the following four characteristics:
- Recurring in paroxysmal attacks lasting from a fraction of a second to 2 min
- Severe intensity
- Sharp, stabbing, blasting, or electric shock-like in nature
- Precipitated by innocuous stimuli to the affected side of the face
Sweet diagnostic criteria
- Pain is paroxysmal.
- The pain may be provoked by a light touch to the face (trigger zones).
- The pain is confined to the trigeminal distribution.
- The pain is unilateral.
- The clinical sensory examination is normal.
Clinical manifestation
- Site of pain: Unilateral facial pain; gums, lips, cheek, chin
- Onset: Sudden, paroxysmal
- Characteristics: Lancinating, cutting, stabbing
- Radiate from angle of mouth, Ear(v3), Eyes(v2), Nose (v1)
- Associated with winses so called as ‘tic douloureux
- Timing: In a few seconds, attacks can follow within minutes.
- Exacerbating factor /Trigger factors:
- Movement allodynia: Smiling, talking, chewing, swallowing
- Tactile allodynia: Touch, face washing, shaving
- Severity: Excruciating pain
Differential diagnosis
- Dental causes
- Temporo-Mandibular Disorders (TMD)
- Disorders of salivary glands
- Maxillary sinusitis
- Cluster headache
- Glossopharyngeal neuralgia
- Post-herpetic neuralgia
- Nervus intermedius neuralgia
- Tolosa-Hunt syndrome
- Multiple sclerosis
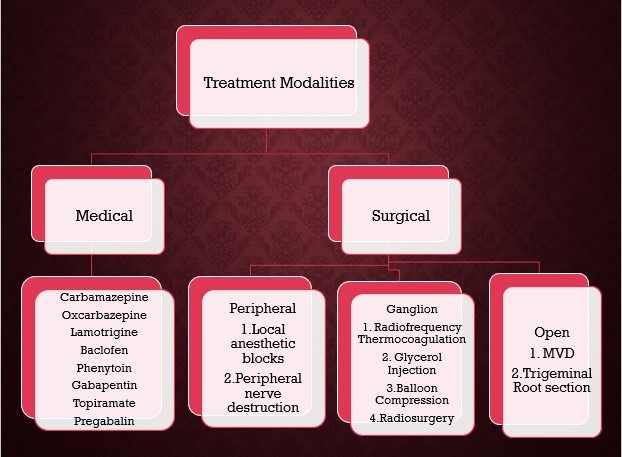
Treatment
Disclaimer- The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of M3 India.
About the author of this article: Dr Dhyey Saradhara is a practising dentist and an oral and maxillofacial surgeon from Surat.
-
Exclusive Write-ups & Webinars by KOLs
-
Daily Quiz by specialty
-
Paid Market Research Surveys
-
Case discussions, News & Journals' summaries