Revised Immunisation Schedule by The Indian Academy of Paediatrics
M3 India Newsdesk Nov 25, 2022
The IAP Advisory Committee on Vaccines and Immunisation Practices (ACVIP) reviewed and analysed new advancements in the field of vaccination in order to revise the IAP Immunisation Timetable for 2020–2021. Details regarding it are provided in this article.
Recommendations for the IAP immunisation schedule for 2020–21 include significant adjustments and modifications
Polio immunisation
- At 4-6 years old, a booster dose of the injectable polio vaccine (IPV) is advised.
- The importance of IPV in the immunisation schedule is re-emphasised.
Inactivated influenza vaccines
For all kids older than 6 months, an inactivated influenza vaccine dose of 15 mcg (0.5 mL) is advised.
Varicella vaccine
Preferably, the second dosage of the varicella vaccine should be given three to six months after the first dose.
New vaccines introduction
- DTaP/IPV combination vaccine: Tetraxim
- Quadrivalent conjugate meningococcal vaccine: Menveo
- Monoclonal antibody cocktail for post-exposure prophylaxis of rabies: Twinrab
- Conjugate (CRM 197) typhoid vaccine: Typhi BEV
- 10-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine: Pneumosil
AP-ACVIP recommendations on newer vaccines
- Accepts the Menveo vaccine's application to people between the ages of two and fifty-five. This vaccination should only be used under specific circumstances, as previously stated.
- Permits the use of the Typhibev vaccination for those older than 6 months and younger than 45 years. There isn't any advice regarding a booster dose.
- The use of Rabis recommended mAbs over RIGs in category 3 bites management. Human monoclonal rabies antibody (Rabishield) and murine cocktail monoclonal rabies antibodies (Twinrab), both are available in India and approved for the post-exposure management of suspected rabies exposure.
- Tetraxim can be used for the second DPT/IPV booster shot at 4-6 years of age.
- Approves the use of Pneumosil till 2 years of age in a 3+1 schedule, with the booster administered between 12-18 months.
- The ACVIP does not currently advise the use of Pneumosil beyond the age of 2 years due to the lack of studies in the 2–5 years age group.
ACVIP recommendation
- Children who have received their initial doses of IPV in accordance with the ACVIP/IAP schedule should receive a booster dose between the ages of 4-6.
- This dose can be given in conjunction with the DPT vaccines if a standalone IPV is not available.
- No child should receive the pentavalent vaccine alone or the bOPV vaccine alone in infancy without also receiving IPV (two doses of fractional dosage intradermal IPV at 6 weeks and 14 weeks or a single dose of full-dose intramuscular IPV/hexavalent combination at 14 weeks). The newborn must be referred to a government healthcare facility for primary immunisation in accordance with the UIP schedule if hexavalent vaccinations are not affordable or readily available.
- The earliest opportunity should be used to administer at least one dose of an IPV/IPV combination vaccination intramuscularly to infants and young children born after the transition (25 April 2016) who have not received IPV in any schedule.
- The ACVIP recommends using a standard dose schedule for inactivated influenza vaccinations (15 g/0.5 mL) for all kids above the age of six months.
- The second dose of varicella vaccine should be preferably administered 3-6 months after the first dose.
IAP recommended vaccines for high-risk children vaccines
Meningococcal vaccine
- Japanese Encephalitis (JE) vaccines
- Oral Cholera vaccine
- Rabies vaccine
- Yellow fever vaccine
- Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine (PPSV 23)
High-risk conditions
- Immunodeficiency, either inherited or acquired (including HIV infection, immunosuppressive therapy, and radiation)
- Chronic cardiac conditions
- Chronic lung conditions (including asthma if treated with prolonged high-dose oral corticosteroids)
- Chronic systemic diseases: Renal (including nephritic syndrome), haematological, hepatic diseases, diabetes mellitus
- Functional/ anatomic asplenia/hyposplenia
- Cerebrospinal fluid leaks, cochlear implants; for pneumococcal infections
Specific high-risk groups
- Children having pets at the home: Rabies vaccine
- JE endemic areas: Japanese encephalitis vaccine
- During outbreaks: Oral cholera vaccine
- For travellers Rabies vaccine, meningococcal vaccine, and yellow fever vaccine
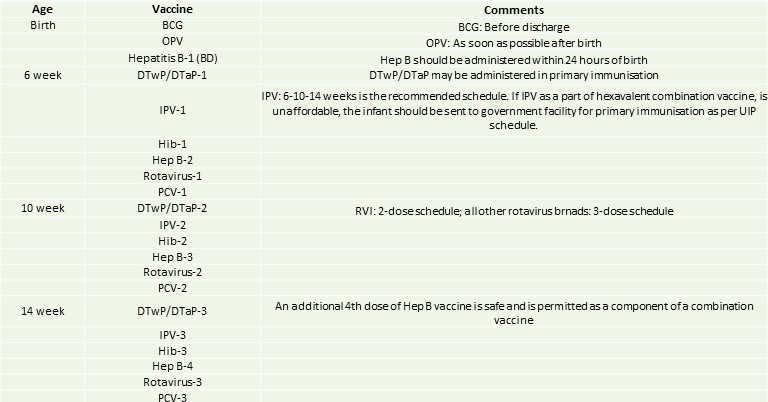
IAP immunisation timetable 2020/21: IAP recommended vaccines for routine use

Click here to see references
Disclaimer- The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of M3 India.
About the author of this article: Dr Monish Raut is a practising super specialist from New Delhi.
-
Exclusive Write-ups & Webinars by KOLs
-
Daily Quiz by specialty
-
Paid Market Research Surveys
-
Case discussions, News & Journals' summaries