Recent Advances in Storage Media for Avulsed Tooth
M3 India Newsdesk Dec 12, 2024
This article highlights tooth avulsion management in children, focusing on storage media like HBSS, milk, and innovations like propolis and Emdogain to preserve PDL cell viability.
The avulsion of teeth is one of the most common acute forms of dental trauma in young children, where root formation is still incomplete.
An avulsion is characterised by the complete displacement of the tooth out of the socket, resulting in a severely compromised neurovascular supply of the tooth, which may lead to loss of vitality. After avulsion, the PDL tissues begin to dehydrate.
As immediate replantation is not always practically possible at the trauma site, an “interim transport” media is often required to maintain the vitality (clonogenic and mitogenic capacity) of PDL cells during the extra alveolar time period.
Storage medium
A storage medium is a physiological solution that closely duplicates the oral environment in order to preserve the survival of PDL cells after avulsion.
Ideal requirement for a storage medium
- It should have osmolarity and pH closer to physiological conditions to maintain the viability of PDL cells.
- It should not produce any antigen-antibody reaction.
- It should be readily available at the site of the accident so that the tooth can be immediately placed into it.
- It should have a longer shelf life.
- It should have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, which reduce inflammation and replacement resorption.
- It should have an antioxidant property which will protect the cells from oxygen radical-mediated damage.
The storage media can be classified as laboratory-prepared and natural sources.
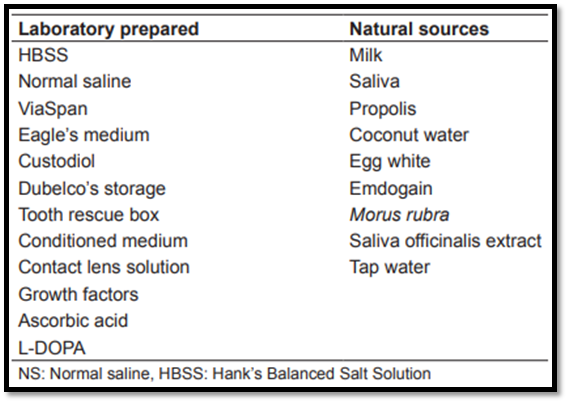
Conventional media
A variety of media have been employed (tap water, saline, saliva) and are traditionally advised (milk, HBSS) as interim transport media for an avulsed tooth.
1. Tap water
- Tap water is an unacceptable storage medium for avulsed teeth due to the least desirable results as it has bacterial contamination, hypotonicity, and a nonphysiological pH of 7.4–7.79.
- Blomolf et al.(1981) found that cultured human PDL cells in tap water for 1 h caused more PDL cell damage than the other physiological and nonphysiological storage media tested.
- As a result, its usage should be limited to situations with short extraalveolar durations.
2. Normal Saline(NS)
- NS is a solution of 0.09% w/v of sodium chloride.
- Despite being compatible with PDL cells, it lacks important minerals such as magnesium, calcium, and glucose, which are required by PDL cells for optimal metabolism.
- Pileggi et al.(2002) conducted a study to evaluate posttraumatic PDL cell viability in NS and found that 55% of living cells after 4h storage and 20% of mortality of cells after 45 min storage.
3. Saliva
- Human saliva is employed as a storage media because it is readily available. It has a pH of 7.4–7.79 and an osmolarity of 30 mOsmol Kg.
- This hypertonic osmolarity causes cell lysis and increased rates of replacement resorption. It also causes swelling and membrane damage of PDL cells of the avulsed tooth if stored for 2–3 h.
- Saliva can be used as a storage medium for a short period, as there can be damage to the cell of the PDL if used for longer than an hour.
- Although readily and most easily available, saliva is not considered an effective interim transport medium.
- Recent literature indicates that saliva may not be a suitable transport medium for the avulsed teeth due to its non-physiologic osmolarity and the presence of microorganisms.
4. Milk
- Because of its physiological osmolarity and nutritional value, milk is regarded as a good interim transport medium for avulsed teeth.
- Its clinical efficacy is considered equivalent to HBSS for maintaining the vitality of the PDL cells of an avulsed tooth for an extended period of time (up to 6 h).
- Marino et al. (2000) conducted a study to determine the ability of long-shelf-life milk to serve as a temporary storage medium for the maintenance of PDL cell viability on avulsed teeth. This demonstrates that low-fat milk and refrigerated milk performed better in terms of sustaining PDL viability for a longer period of time.
- However, the main drawback is the presence of antigens that may interfere with the reattachment process.
5. HBSS
- HBSS was introduced by Hanks in 1975 as a solution for the preservation of tissue culture.
- Among all the storage media, HBSS is considered the gold standard and is often used as a reference medium to deduce the clinical efficacy of other media.
- The American Academy of Endodontics has accepted HBSS as an acceptable medium for avulsed teeth because of its capability to maintain the vitality and proliferative capacity of PDL for an extended period of time (up to 48 h).
- It contains sodium chloride, Dglucose, potassium, calcium chloride, and magnesium sulfate anhydrous. Its both pH (7.4) and osmolarity (280 mOsmol/kg) are ideal. It can preserve the cells and tissues for 24 h.[29] It can maintain the viability of PDL cells for several hours with a success rate of 90%.
- HBSS has no need of refrigeration. HBSS is marked as SaveA-Tooth (Save-A-Tooth; Phoenix-Lazerus Inc., Pottstown, PA, USA), to maintain PDL cell viability. Unfortunately, HBSS is not commonly used in India due to a lack of availability.
Current developments
1. Propolis
- Propolis is a sticky substance derived mostly from the buds of certain coniferous plants. It is an antibacterial and antiinflammatory beehive product.
- Propolis contains antiseptic, antibiotic, antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, antioxidant, anticarcinogenic, antithrombotic, and immunomodulating activities.
- Mori et al.(2010) conducted a study to evaluate propolis as storage media for the avulsed teeth and concluded that the efficacy of the medium was increased if maintained for 6 h because contact with the product is beneficial for cell maintenance.
2. Coconut water
- Coconut water is biologically pure and sterile. It's full of amino acids, minerals, and vitamins. It is known to possess regenerative and antioxidant properties.
- Antioxidant-rich storage media may be more successful for preserving PDL viability.
- Due to its superior properties, coconut water can be advocated as a viable storage medium.
3. Growth factor
- The use of polypeptide growth factors, which function as a potent biological mediator regulating numerous activities of the wound healing, has been suggested for the promotion of PDL regeneration.
- Lynch et al.(1991) demonstrated that short-term application of a combination of platelet-derived growth factor and insulin-like growth factor can enhance the formation of the periodontal attachment apparatus 5–10-fold during the early phase of wound healing.
4. Emdogain (Enamel Matrix Derivatives, EMD)
- Emdogain (Biora, Malmo, Sweden) is a commercial EMD extracted from developing embryonic enamel of porcine origin and contains several matrix proteins. Studies have shown that it can influence the migration, attachment, proliferation capacity, and biosynthetic activity of PDL cells.
- Tooth Rescue Box Dentosafe (Miradent, Germany) is a commercial name for a tooth rescue box that contains a specific cell culture medium made up of amino acids, vitamins, and glucose.
- In the USA, it is marketed as an EMT tooth saver (Phoenix, USA). It has demonstrated the maintenance of the vitality of PDL cells for 48 h at room temperature. If unopened, this medium has a shelf life of 3 years.
Disclaimer- The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of M3 India.
About the author of this article: Dr Neha Kalantri is a practising dentist from Nashik.
-
Exclusive Write-ups & Webinars by KOLs
-
Daily Quiz by specialty
-
Paid Market Research Surveys
-
Case discussions, News & Journals' summaries