Paediatric Nutrition: Best Practices for Healthy Growth and Development
M3 India Newsdesk Dec 05, 2024
This article highlights the importance of pediatric nutrition in fostering lifelong health, providing age-specific dietary guidance from infancy to childhood while addressing common challenges like deficiencies, obesity, and picky eating.
Introduction
Nutrition in early childhood lays the groundwork for lifelong health, influencing growth, immunity, cognitive function, and disease risk. As healthcare providers, helping families establish solid nutrition practices can prevent chronic conditions like obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease in adulthood.
Essential nutritional components in early childhood
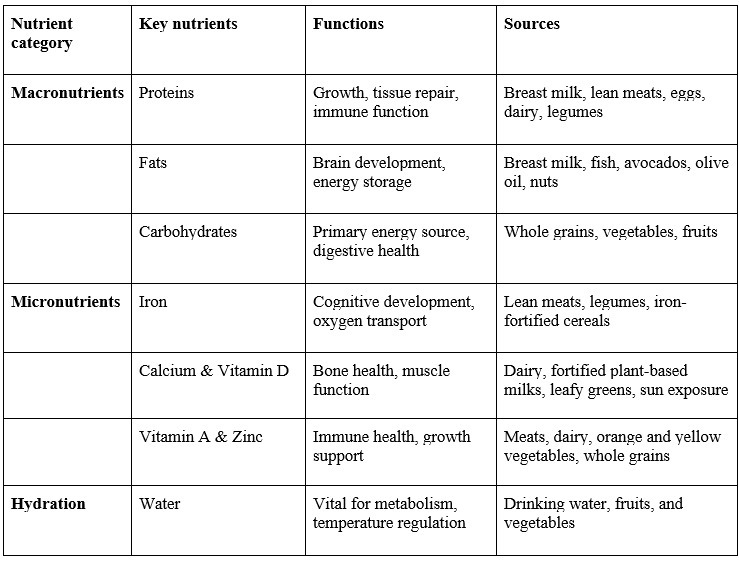
Key nutritional strategies by developmental stage
Nutritional requirements evolve significantly across different developmental stages. Providing tailored guidance based on a child’s age helps meet growth needs while instilling healthy eating habits.
Infancy (0-12 months)
- The foundation of pediatric nutrition is established during infancy, where breastfeeding is considered the gold standard due to its balanced nutrient composition and immune support.
- Breastfeeding exclusively for the first six months, followed by continued breastfeeding alongside complementary foods until at least 12 months, aligns with WHO recommendations. For formula-fed infants, choosing formulas rich in DHA and other EFAs is recommended.
- When introducing solids around six months, iron-rich foods should be prioritised, including pureed meats, iron-fortified cereals, and legumes. Foods should be introduced one at a time, with a focus on variety to encourage broad nutrient intake and reduce the risk of allergies.
Toddlers (1-3 years)
- During the toddler years, nutrition emphasises establishing balanced, nutrient-dense meals that include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy proteins. Healthy fats, such as those found in avocado and olive oil, continue to support brain development.
- Toddlers can often be selective eaters, making it essential for caregivers to provide consistent, positive exposure to a variety of foods without pressure, which encourages willingness to try new foods over time.
- To avoid excessive sugar intake, caregivers should limit sugary drinks and processed snacks. Instead, offer whole fruits, unsweetened yoghurts, and other nutrient-dense snacks that support energy needs without contributing empty calories.
Preschool to school-aged children (4-12 years)
- As children enter preschool and beyond, their energy needs increase due to higher levels of physical activity and continued growth. Balanced meals with proper portion sizes become essential.
- Encourage meals that cover all food groups, such as whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of fruits and vegetables.
- In this stage, routine mealtimes and positive food environments help children internalise healthy eating habits. It’s also crucial to limit highly processed foods and emphasise whole, unprocessed foods, which support stable blood sugar levels, better focus, and higher energy for learning and activities.
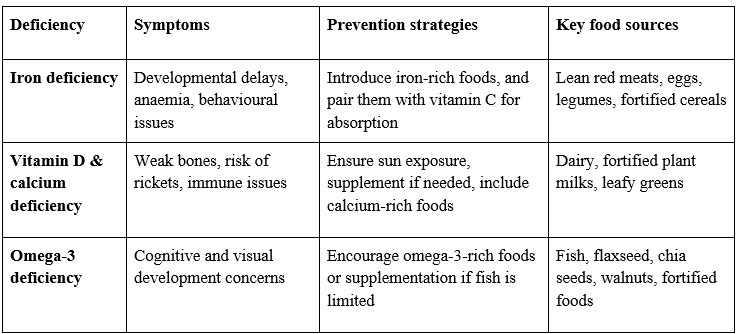
Preventing and managing common nutritional deficiencies
Childhood obesity: Early prevention and intervention
Childhood obesity is an increasing concern, linked with early metabolic abnormalities and elevated risk of chronic diseases later in life. Preventive measures in early childhood focus on fostering balanced diets and encouraging physical activity.
Healthcare providers can advise caregivers on:
- Age-appropriate portion sizes: Overeating often starts with portion sizes that exceed a child’s actual needs. Educating parents on serving sizes for young children is crucial for prevention.
- Limiting sugar intake: Sugar-sweetened beverages and processed snacks contribute empty calories, raising obesity risk. Recommending water, whole fruits, and low-fat dairy as alternatives provides healthier options.
- Promoting physical activity: Daily physical activity should be encouraged from a young age, whether through play, organised sports, or outdoor activities, to support muscle development, healthy weight, and cardiovascular health.
Fostering healthy eating behaviours
Developing a positive relationship with food in early childhood can have lasting effects. Healthcare providers play an essential role in guiding parents toward best practices for fostering healthy eating habits.
Parental guidance and role modelling
Children mimic behaviours, so parental modelling of healthy eating habits is impactful. Educating parents on balanced, family-style meals that include a variety of nutrient-dense foods can set an example for children to follow.
Addressing picky eating
Picky eating is common among young children and can be addressed by introducing a wide range of foods without pressuring the child to eat specific items. A calm, consistent approach can gradually increase acceptance of new foods, particularly if children are exposed to them repeatedly in a positive setting.
Mindful eating practices
Teaching children to recognise hunger and fullness cues can help prevent overeating and support self-regulation. Simple practices, such as eating slowly and without distractions, promote mindful eating, leading to healthier eating habits over time.
Pediatric nutrition forms the bedrock of lifelong health, influencing growth, development, and disease risk. By emphasising balanced, nutrient-dense foods and instilling positive eating habits from infancy through childhood, healthcare providers can support families in setting their children up for long-term well-being. Effective pediatric nutrition strategies reduce deficiencies, encourage healthy weight management, and help children develop a lasting, healthy relationship with food.
Disclaimer- The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of M3 India.
The author of this article: Ms Rutambhara Nhawkar is a Clinical Dietician, M. Sc. (Clinical Nutrition & Dietetics), Certified Diabetes Educator and a medical writer from Pune.
-
Exclusive Write-ups & Webinars by KOLs
-
Daily Quiz by specialty
-
Paid Market Research Surveys
-
Case discussions, News & Journals' summaries