Myths and facts about kidney diseases: Dr NK Hase
M3 India Newsdesk Apr 18, 2022
This article speaks about some facts and myths that are largely believed about kidney diseases and fills in the gap of knowledge in kidney care.
Myth1: Kidney diseases are very rare.
Facts:
- The incidence of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is increasing. It is a major public health problem worldwide.
- 850 million people worldwide are now estimated to have some form of kidney disease.
- 10% of people worldwide have CKD. An estimate suggests that 9 out of 10 of those are unaware of their disease.
- 2.6 million received dialysis or transplantation worldwide. The number is projected to increase by 5.4 million by 2030.
- Kidney disease is projected to be the 5th leading cause of death by 2040.
- The cost of dialysis and transplantation consumes 2% to 3%of the annual health care budget in high-income countries.
- In India below the poverty line, people are supported by the government and others have to spend from their pockets.
- The best solution to reduce the economic burden is the prevention of CKD and its progression to end-stage kidney disease (ESKD).
Myth 2: The patient does not have any symptoms, is passing a good amount of urine, hence unlikely to have chronic kidney disease.
Facts:
- In the early stages of the disease patients do not have symptoms. The disease is detected by doing investigations like urine creatinine and estimated GFR.
- Urine output may be normal or increase due to the loss of concentration ability of the kidney.
- There may be an increased frequency at night(nocturia) -this is one of the early symptoms of CKD.
Myth 3: Testing for kidney diseases is costly and cumbersome.
Facts:
- Screening for kidney disease is easy and not costly.
- Simple urine testing for albumin/proteins in spot sample & estimating Glomerular Filtration rate (eGFR)from serum Creatinine will detect renal disease.
- Albuminuria or Proteinuria is an early marker of structural damage to the kidney and serum Creatinine & eGFR are markers of functional impairment.
- Structural damage and/or functional impairment persisting for more than 3 months is called CKD.
- All high-risk patients for CKD, diabetics, hypertensive, heart disease, a patient having recurrent urinary tract infections, recurrent stones and age more than 50 years should undergo screening for CKD by urine and creatinine testing to detect the disease early annually even though they do not have symptoms.
Myth 4: Normal Serum Creatinine and Urine examination rule out kidney diseases.
Facts:
- Serum Creatinine starts increasing when more than 50% of kidney function is lost.
- The early functional impairment will be detected by estimating GFR (eGFR) from creatinine or Measuring the GFR by Creatinine clearance or plasma disappearance of iohexol, iothalamate or DTPA.
- Urine albumin is absent in tubular dysfunction or tubulointerstitial injury.
Myth 5: Kidney involvement in diabetes is always associated with proteinuria followed by decreased GFR.
Facts:
- Albuminuria is the earliest marker of kidney involvement in diabetes. All Compartment of the kidney i.e. Glomerular, tubulointerstitial, microvascular, tubular, and urinary tract can get involved.
- Glomerular involvement is called diabetic nephropathy. Diabetic Kidney disease (DKD)includes a whole spectrum of kidney involvement. It is now increasingly recognized that the non-proteinuric phenotype of DKD is almost 40-50%.In DKD decreased GFR may not be preceded by or associated with proteinuria.
- The absence of albuminuria/proteinuria does not rule out DKD.
Myth 6: If patients are at a risk for a kidney disease, there is nothing you can do. They will develop chronic kidney disease.
Facts:
- Not everyone who is at risk will get CKD. Only 40% of diabetes will likely get CKD.CKD can be prevented or if detected early progression can retarded.
- Studies have proven that tight control of blood glucose in diabetes, control of BP in hypertensive patients, treating recurrent urinary tract infections, relieving urinary tract obstruction in time, and avoiding prolonged use of NSAIDs may prevent or retard the progression of CKD.
Myth 7: Medicine can bring down serum creatinine. Give medication to reduce creatinine level.
Facts:
- Serum creatinine is a functional marker of the kidney. Creatinine level suggests how much the kidney is functioning. Serum creatinine levels will come down when kidney function of kidney improves.
- There is no medication available that will decrease Creatinine. Treatment will be directed towards the cause and risk factors for CKD like control of diabetes, control of BP, avoiding smoking, avoiding nephrotoxins and regular exercise.
Myth 8: Patients with CKD should avoid proteins, fruits, and vegetables, and restrict fluid intake.
Facts:
- CKD Patients should avoid a high protein diet i.e. protein intake of more than 1.3g/kg/day. And not stop proteins.
- The majority of Indians are vegetarians they are already taking low proteins and not decreasing protein intake further. Protein Calorie malnutrition is one of the risk factors for poor outcomes in CKD.
- CKD patients with high potassium and tendencies toward high potassium should avoid high potassium-containing fruits and vegetables (oranges &orange juice, melons, apricots, bananas, potatoes, cooked spinach, cooked broccoli, beans, legumes (Low potassium alternatives are: apples, pineapple, plums, pears, guavas, strawberries cabbage, boiled cauliflower).
- Fluid is restricted only in patients with oedema. Other patients may take fluid as per their thirst.
Myth 9: The only definitive treatment for CKD is dialysis.
Facts:
- Dialysis is indicated when CKD progresses to end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) i.e. when kidney function goes below 5%.
- The patient develops uraemic symptoms –nausea vomiting, anorexia weight loss, fluid overload, refractory acidosis, hyperkalemia ---are absolute indications to initiate dialysis.
- Not all patients progress to ESKD, progression can be retarded or prevented.
- A kidney transplant is the treatment of choice for ESKD.
Myth 10: Dialysis is a death sentence. Once dialysis, always dialysis!
Facts:
- Before 1960 ESKD was synonymous with death. The discovery of dialysis has changed survival dramatically. Dialysis is not a death sentence it is a life-sustaining therapy.
- Dialysis (Haemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis ) does the excretory & regulatory functions of the kidney. It is an artificial kidney.
- Dialysis adds useful years to life. A 5 year survival is 50%.
- Dialysis support is temporary in acute kidney injury.
Myth 11: A kidney transplant is not successful and it is a costly therapy.
Facts:
- A kidney transplant is no more an experimental therapy. It is a well-established therapy for patients with ESKD.
- A kidney transplant is the treatment of choice as survival is longer than dialysis, good quality of life, and all the functions of the kidney are replaced. Full rehabilitation. The overall cost is less than dialysis. It is the most cost-effective therapy.
- A renal transplant is not a cure. The patient will need to take lifelong immunosuppressive drugs.
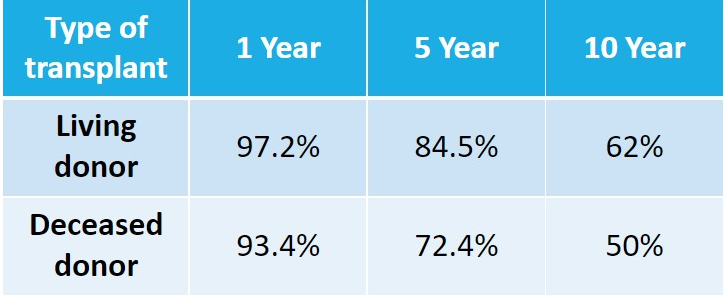
Survival rate in kidney transplant
Disclaimer- The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of M3 India.
The author Dr NK Hase is a Director of Clinical Nephrology & Transplant working at Jupiter Hospital, Thane and a former Professor & Head of the Department of Nephrology at Seth GS Medical College and KEM Hospital, Mumbai.
Only Doctors with an M3 India account can read this article. Sign up for free or login with your existing account.
4 reasons why Doctors love M3 India
-
Exclusive Write-ups & Webinars by KOLs
-
Daily Quiz by specialty
-
Paid Market Research Surveys
-
Case discussions, News & Journals' summaries