Common Ear Infections in Adults: How to Approach Ear Related Complains
M3 India Newsdesk Jun 01, 2023
This article examines problems such as ear pain, discharge, and diminished hearing and emphasises how often the ear is neglected in comparison to other body regions. It also looks at what contributes to these issues, like exposure to loud noises, poor cleaning techniques, and noise pollution.
Common ENT complaints
Increasing noise pollution, usage of earbuds, and exposure to loud noises lead to early degeneration of the sensory organ of the corti leading to hearing loss. Also, a false sense of cleanliness leads to an increase in the usage of cotton swabs to remove wax leading to trauma in the ear canal leading to otitis externa.
The following are the most common ENT complaints:
Earache
Also known as otalgia. Otalgia refers to pain experienced in and around the ear. Ear pain is a very common otological complaint. Finding the cause is crucial for treatment.
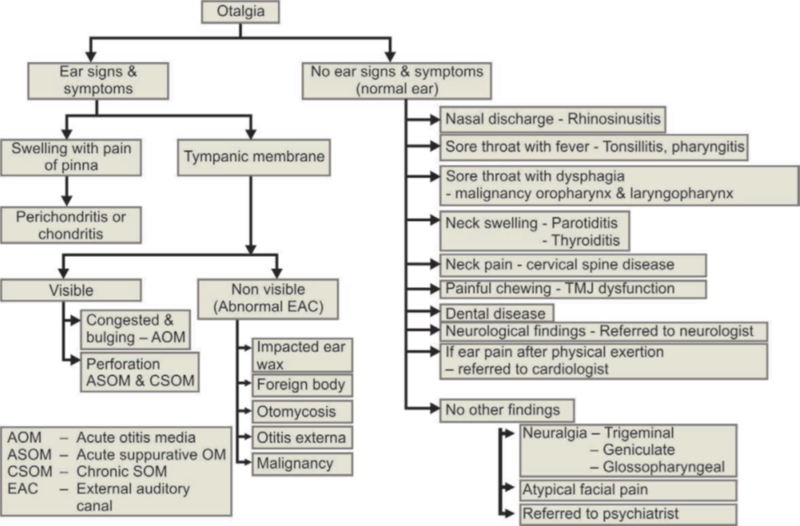
Flow chart for clinical diagnoses of causes of otalgia
Otorhhea
Refers to discharge from the ear, which is a very common otologic complaint.
Types of discharge and their causes
- Mucopurulent: Acute suppurative otitis media (ASOM) and chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM)
- Serous: Eczematous otitis externa (OE)
- Sanguineous (blood-tinged): ASOM, granulations, trauma, tumours
- Putrid (foul smelling): Cholesteatoma
- Watery: Watery otorrhea, which may be copious, subtle or intermittent, suggests a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak.
Otitis externa
Externa is an inflammation of the EAC.

1. Acute Otitis Externa
The underlying epithelium is exposed to water, infection, and other pollutants when the hydrophobic ceruminous coating of the EAC is removed, which causes increasing erythema and oedema.
Predisposing factors
- Warm humid environment: Excessive sweating changes the canal pH to alkaline, which favours bacterial growth.
- Obstruction of EAC: Stenosis, exostoses, impacted wax.
- Ear trauma: Use of cotton-tip swabs, irrigators for wax removal, in-the-canal hearing aids, digital ear thermometers, and unskilled instrumentation.
- Water contamination of EAC: Usually swimming-related.
Clinical features
- Presenting complaints: Otalgia and otorrhea. Ear pain may be aggravated with jaw movements. Itching is present in some cases.
- Early stage: An erythematous canal with scant discharge.
- Later on: Edematous and exquisitely tender canal occluded with purulent squamous debris.
- In severe cases: Enlarged and tender regional lymph nodes and periauricular cellulitis.
- No additional systemic signs and symptoms.
2. Chronic Otitis Externa
- No prior history of trauma or water contamination.
- Usually not painful.
Complications of otitis externa
- Cellulitis: It presents as an erythematous ear. There is no induration like perichondritis. Treatment is with a systemic antistaphylococcal agent.
- Perichondritis or Chondritis
- Medial canal fibrosis: In chronic otitis externa (COE), a thick fibrous scar may obstruct the deep aspect of EAC. TM appears lateralised with an absence of typical landmarks. Surgical treatment consists of excision of the fibrous scar followed by canaloplasty with split-thickness skin graft and if needed tympanoplasty.
3. Malignant otitis externa
This rare OE of immunocompromised patients is an aggressive and potentially fatal infection, which progressively spreads to the skull base and intracranial structures.
Causative microorganisms: Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the most common. Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis are rare.
Immunocompromised patients: Elderly diabetics, HIV/AIDS, myeloid malignancies, anticancer drugs and organ transplant recipients.
In the case of recurrent furunculosis, diabetes should be excluded, and attention paid to the patient’s nasal vestibules which may harbour staphylococci and the infection transferred by the patient’s fingers. Staphylococcal infections of the skin as a possible source should also be excluded and suitably treated.
Chronic otitis media
It can be of mainly two types:
(a) Tubotympanic: having copious, non-foul-smelling discharge with a permanent perforation in the tympanic membrane.
(b) Atticoantral: having scanty, foul-smelling discharge: denoting bone eroding process. It is treated as an emergency and cured promptly.
Case studies
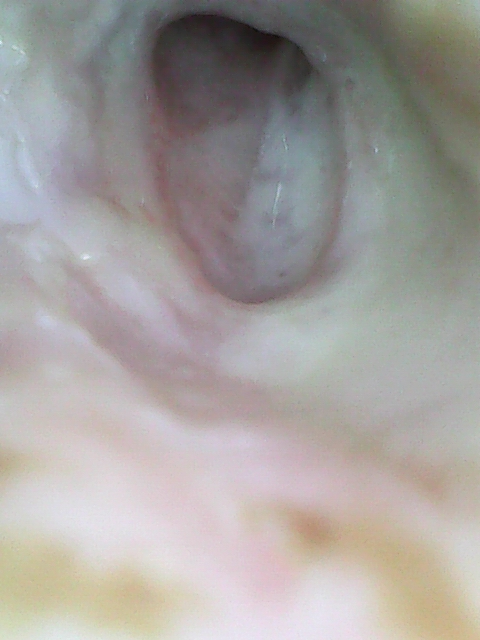
Case 1
A male patient working as a farmer 26 years old came to ENT OPD with a complaint of ear discharge for 10 years. History of intermittent ear discharge aggravating with cold weather, audiometry showed moderate conductive hearing loss.
Diagnosis: On otoscopy large perforation was seen.
Treatment: The patient was operated on with tympanoplasty with near-normal hearing.
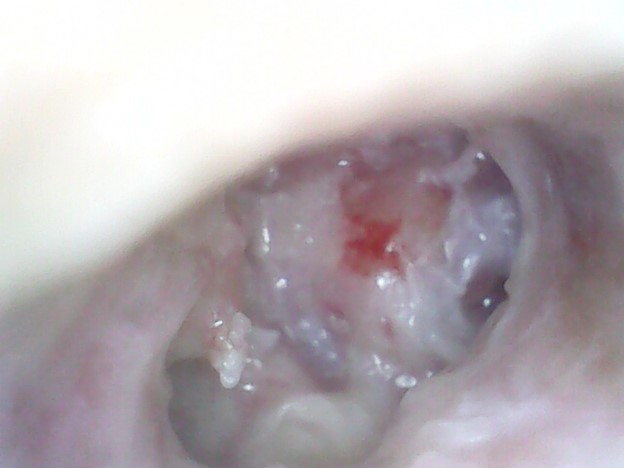
Case 2
A 20-year-old female patient presented to ENT OPD with complaints of headache, and ear discharge which was foul smelling, scanty and occasionally blood-tinged.
Diagnosis: Audiometry showed mild conductive hearing loss and on otoscopy grade 3 attic retraction with cholesteatoma flakes.
Treatment: The patient was treated with surgery: Modified radical mastoidectomy.
The above-discussed entities are the most common ear infection in adults per se. But decreased hearing with tinnitus is on the rise. So utmost care should be taken to avoid noise pollution and trauma to the ear.
Disclaimer- The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of M3 India.
About the author of this article: Dr Tosha Shah MS is a Senior Consultant practitioner at Dhiraj Hospital, Vadodara.
-
Exclusive Write-ups & Webinars by KOLs
-
Daily Quiz by specialty
-
Paid Market Research Surveys
-
Case discussions, News & Journals' summaries