Diabetes Complications: Neuropathy, Nephropathy, and Retinopathy
M3 India Newsdesk Sep 20, 2024
Diabetes mellitus can be defined as a metabolic disorder characterised by hyperglycemia that develops as a consequence of defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. This article explains the microvascular complications of diabetes, associated risk factors and management.
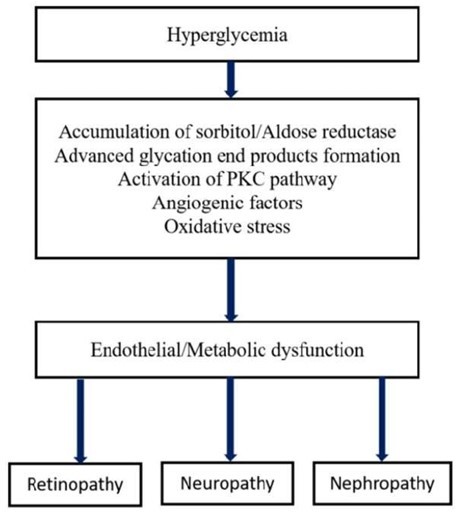
Diabetes mellitus results in increased concentrations of glucose in the blood, which in turn damages many of the body’s systems, particularly the blood vessels and nerves. Microvascular complications of diabetes include- retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy.
Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy can be defined as the progressive loss of nerve fibre function in patients with diabetes after the exclusion of other causes. The majority of patients remain asymptomatic in the early course of the disease. Generally, numbness, tingling or pain in the toes, feet, legs, hands, and arms are the common symptoms.
Risk factors for diabetic neuropathy:
- Poor glycemic control
- Advanced age
- Hypertension
- Dyslipidemia
- Smoking
- Heavy alcohol intake
- Long duration of diabetes
- Vitamin deficiency
Management of symptomatic neuropathy:
- Exclude non-diabetic etiologies
- Achieve glycemic control
- Tricyclic drugs (eg: amitryptiline)
- Anticonvulsants (eg: pregabalin, gabapentin)
- Opioids (eg: tramadol)
Preventive measures for diabetic neuropathy
- Achieve glycemic control
- Cessation of smoking
- Footcare and foot checkup
- Modest alcohol intake
- Maintaining normal blood pressure
- Healthy diet
- Regular exercise
- Regular follow-up
Nephropathy
Diabetes is one of the leading causes of CKD. It is characterised by persistent albuminuria (>300 mg/day) that is confirmed on at least two occasions 3-6 months apart, progressive decline in GFR and elevated arterial blood pressure in patients of diabetes. Clinical features include changes in the frequency and quantity of urine, changes in the appearance of urine, and pedal oedema.
Risk factors of diabetic nephropathy:
- Hyperglycemia
- Hypertension
- Smoking
- Dyslipidemia
- Proteinuria due to other disease
Goals for treatment of diabetic nephropathy:
- Low-protein diet
- Strict glycemic control (GHbA1c)
- Smoking cessation
- Control dyslipidemia
- ACE inhibitors/ ARB use for better HTN control
Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is the most frequent ocular complication of diabetes and is the leading cause of preventable blindness among people 20-74 years old. Small blood vessel injury to the retina, the rear layer of the eye, is the cause, and it progresses to blindness. Initially, diabetic retinopathy might cause no symptoms. In non-proliferative and pre-proliferative retinopathy, blurry vision secondary to macular oedema occurs in some patients.
Risk factors associated with diabetic retinopathy:
- Hyperglycemia and long duration of disease
- Hypertension
- Dyslipidemia
- Smoking
- Rapid correction of glycemia- pregnancy, insulin pump therapy
Management of diabetic retinopathy
- Identification of patients in early stages and planning treatment accordingly.
- Fundus photography and telemedicine for screening.
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT) helps in the diagnosis of Diabetic macular oedema (DME).
- Laser photocoagulation and vitrectomy.
Prevention of diabetic retinopathy
- Strict glycemic control, and blood pressure management.
- First ophthalmologic examination when diabetes is diagnosed and then yearly routine follow-up.
- Pregnant with pre-existing diabetes: first examination before conception and during the first trimester and follow-up as advised by the physician.
Conclusion
A combined approach of tight glycemic control, aggressive BP control and cholesterol reduction will help reduce disease progression. Patients with diabetes and their healthcare professionals need to be vigilant and detect microvascular disease at an early stage to avoid potentially devastating complications.
Disclaimer- The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of M3 India.
About the author of this article: Dr Rinkal Solanki is a Consultant Diabetologist at Madhushanti Diabetes Clinic, Surat.
-
Exclusive Write-ups & Webinars by KOLs
-
Daily Quiz by specialty
-
Paid Market Research Surveys
-
Case discussions, News & Journals' summaries