Crowns in Paediatric Dentistry
M3 India Newsdesk Aug 09, 2024
A dental treatment that fully encloses or caps a tooth or dental implant is known as a crown or dental cap. Today, many options are available for aesthetic crowns, but our goal should be a healthy beautiful smile rather than just a beautiful white smile.
Prefabricated crowns
Prefabricated crowns have been widely used in paediatric dentistry for 50 years.
The three recently most used ones are:
- Preformed metal crowns
- Resin-veneered stainless steel crowns
- Strip crowns
More aesthetic solutions include:
- Pre-veneered crowns
- Zirconia crowns
The use of paediatric crowns involves proper preparation of the tooth crown for it to fit well, or it may involve no preparation using Hall’s technique.
Indications
- A primary tooth with more than two surfaces is destroyed due to caries.
- A tooth which has undergone pulp therapy i.e. following pulpotomy or pulpectomy.
- For teeth with extensive developmental abnormalities of the enamel or dentin.
- After traumatic injuries to teeth involving a significant portion of the crown.
- For extensive carious destruction of young permanent teeth requiring full crown restorations.
- In high caries risk children.
- As an interim restoration for posterior teeth with cracked tooth syndrome.
- As an interim and affordable restorative option, considering financial conditions.
- Patients of Bruxism.
- Use as an abutment for a space maintainer.
Final crown selection
The final crown selection is based upon clinical examination and shall take into consideration the following factors:
- Developmental status of the dentition
- Caries-risk assessment
- Operator’s preferences
- Aesthetic demands by parents and the child
- The child's behaviour & ability to cooperate for treatment
- The amount of tooth structure present and its dimensions
- Moisture and haemorrhage control
- Patient’s oral hygiene status
- Likelihood of recall and Family compliance
- Cost
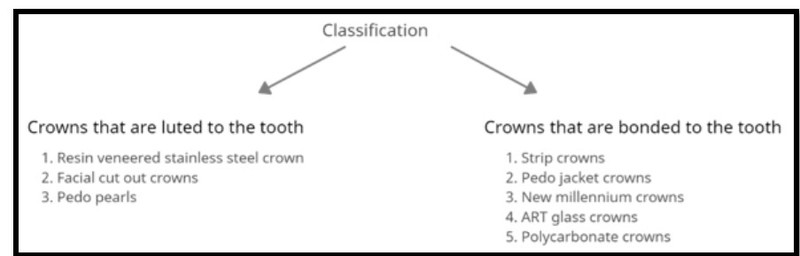 Classification of crowns by Sahana S et al.
Classification of crowns by Sahana S et al.
Types of aesthetic crowns
1. Open-faced stainless steel crown
This is a form of the use of SSCs in the anterior section of the dental arch
Procedure:
- Adapting a proper SSC.
- If needed, the crown is trimmed, crimped, and polished.
- After the crown is cemented and the cement sets, the labial wall of the crown is cut out and luting cement is partially removed to create undercuts.
- Then, the space is filled with a more aesthetic material like composite.
Indications:
- Crown fracture
- Pulp protection
Contraindications:
- Allergy or vulnerability to nickel.
- Uncooperative patient.
- A primary tooth near its exfoliation time.
- A radiograph shows resorption of more than half of the tooth root.
- Tooth fracture level below the gingival margin.
Advantage:
They have better aesthetics compared to traditional SSCs.
Disadvantages:
- It takes a while to complete and needs a dry restoration area.
- Restoration may have poor colour stability.
- Metal margins of the crown might still be visible.
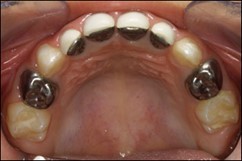
Open-faced stainless steel crown
2. Pre-veneered stainless steel crowns
- These were introduced in the mid-1990s.
- The stainless steel anterior crown is covered on its buccal or facial surface with a tooth-coloured coating of polyesters, composite and epoxy resins.
- They are aesthetic crowns with the strength and durability of stainless steel crowns.
- Some commercially available products are Cheng crowns, Nusmile crowns, Kinder Krowns, Whiter biter crowns etc.
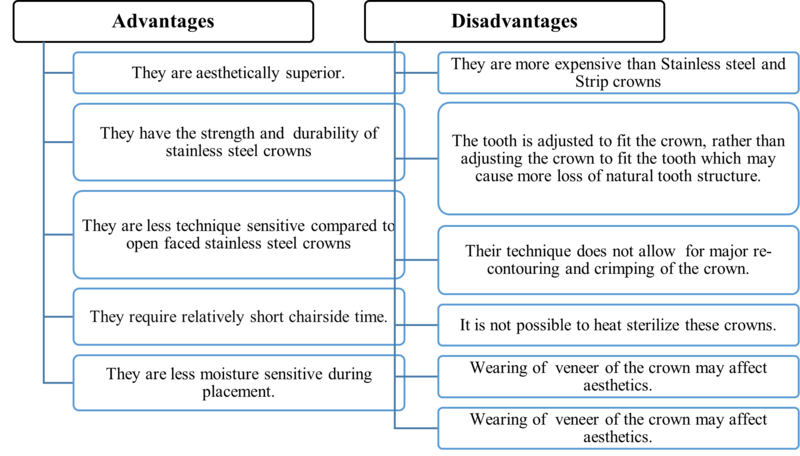
Pre-veneered stainless steel crowns: Advantages and disadvantages
3. Composite strip crowns
- Strip crowns are transparent plastic forms used to simplify work within upper incisors.
- They can be filled with both chemical and light-curing composite.
- Once the composite is set it can be easily removed leaving a smooth surface.
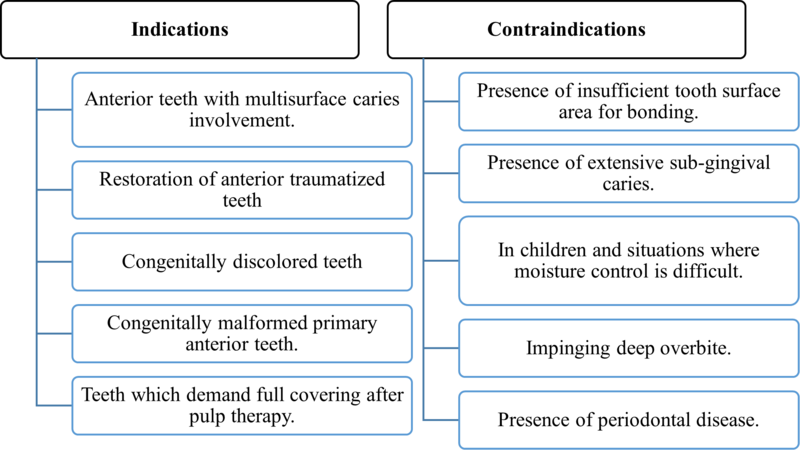 Composite strip crowns: Indications and contraindications
Composite strip crowns: Indications and contraindications
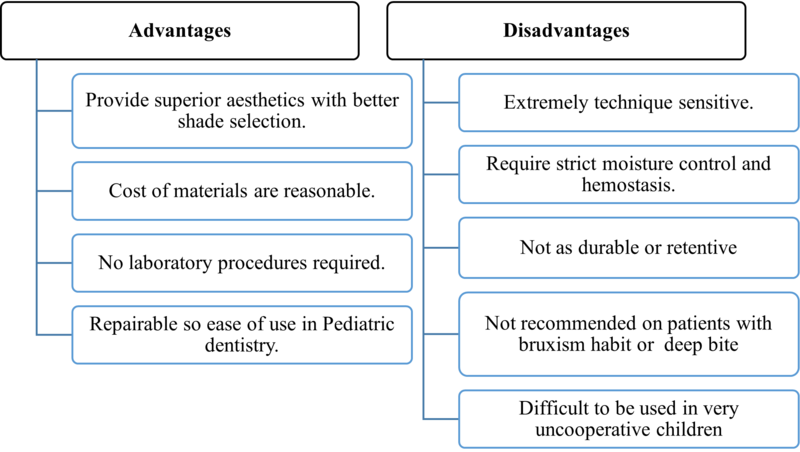
Composite strip crowns: Advantages and disadvantages
4. Polycarbonate crowns
- They are preformed acrylic resin crowns which are thermoplastic resins molded by heat under high pressure into the required shape and form.
- In clinical usage, these resin shells are luted to the tooth using self-cured acrylic resin.
 Polycarbonate crowns
Polycarbonate crowns
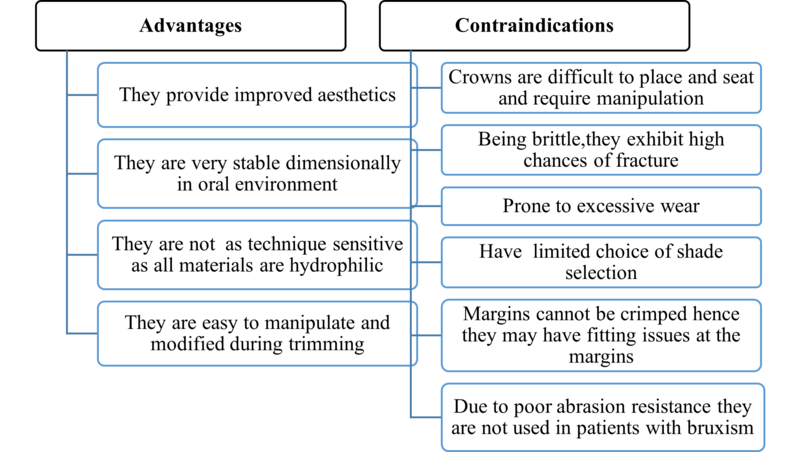 Polycarbonate crowns: Advantages and contraindications
Polycarbonate crowns: Advantages and contraindications
5. Zirconia crowns
- Zirconia is a dental ceramic material that is strongest and aesthetically superior.
- It became commercially available in 2008.
- Some commercially available products are Nusmile Zr, Kinder crowns Zr, EZ Pedo crowns etc.
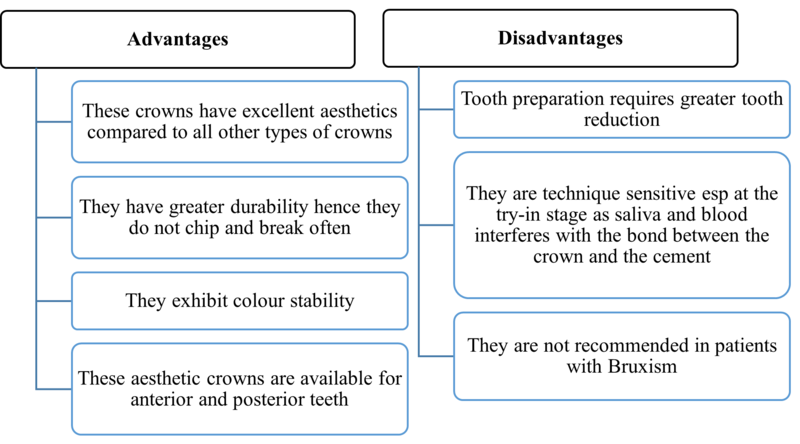 Zirconia crowns: Advantages and disadvantages
Zirconia crowns: Advantages and disadvantages
Recent advances
Recent advances include:
- Pedo Jacket crowns
- Pedo Pearls
- New Millennium crowns
- Artglass crowns
- Bioflex crowns
1. Pedo Jacket crowns
These are modifications of Strip crowns where the ‘Jacket’ is made up of a tooth-coloured copolyester material which is then filled with resin and left on the tooth after polymerisation instead of being removed.
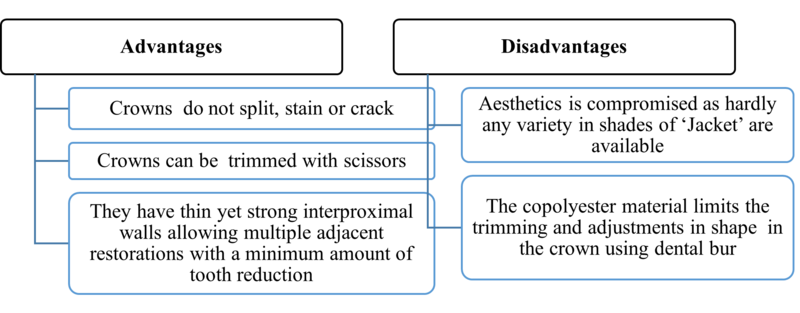
2. Pedo pearls
These are metal crowns, made up of heavy gauge aluminium coated with tooth-coloured epoxy resin.
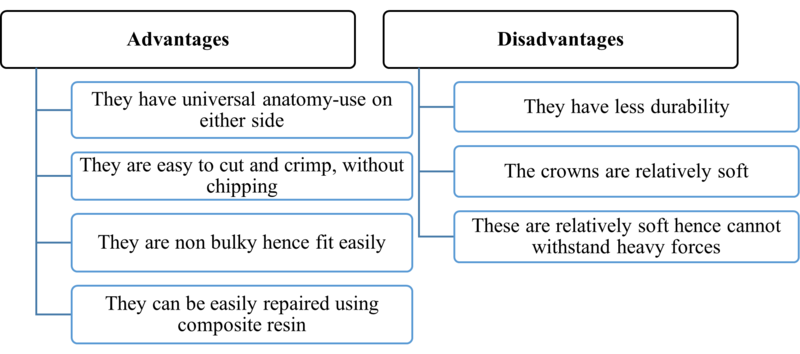
3. New millennium crowns
These crowns are made up of lab-enhanced composite resin material but are similar to strip crowns.
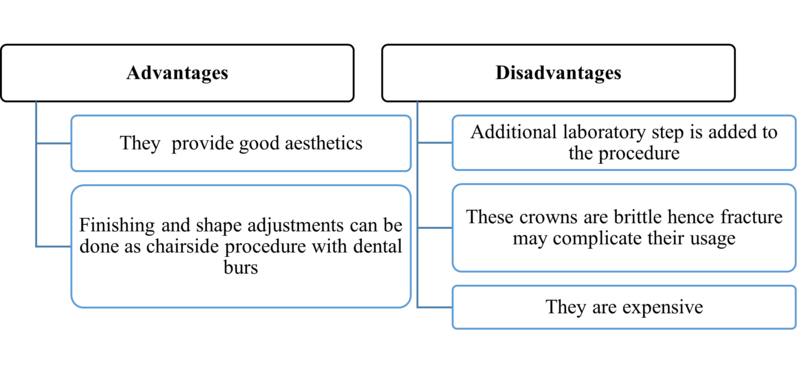
4. Artglass crowns
- They are also called glasstech crowns.
- These are preformed crowns containing multifunctional methacrylate with a highly cross-linked structure formed by glass and silica particles.
- Their longevity is comparable to that of porcelains.
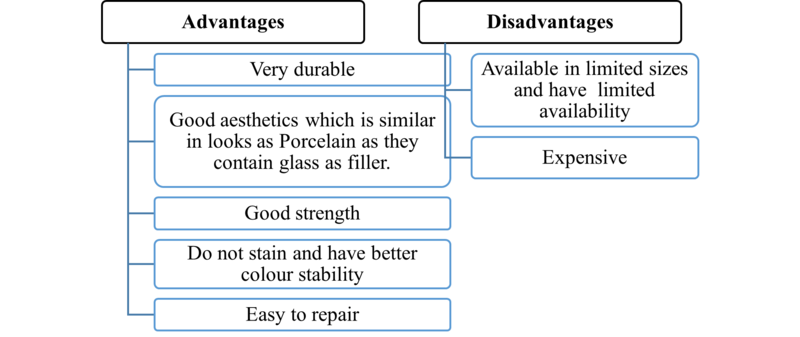
Conclusion
Currently, many options are available for restoring primary and young permanent teeth in paediatric dental practice. The various factors are key in deciding the right choice as per the case. Operator’s preferences, aesthetic demands by the patient and parents, the child’s behaviour and moisture control, are all variables which affect the decision and outcome of the type of ‘Crown’ that is chosen for the restorative treatment.
Disclaimer- The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of M3 India.
About the author of this article: Dr Neha Kalantri is a practising dentist from Nashik.
-
Exclusive Write-ups & Webinars by KOLs
-
Daily Quiz by specialty
-
Paid Market Research Surveys
-
Case discussions, News & Journals' summaries