Applications of Generative AI: Information Retrieval for Clinicians
M3 India Newsdesk Aug 27, 2024
The article discusses how Generative AI (GenAI) can transform Indian healthcare by enhancing information retrieval, standardising medical data across languages, and reducing clinical errors.
The healthcare industry in India is about to experience a digital revolution, with vast amounts of patient data being generated and stored electronically. While this wealth of information has the potential to greatly improve patient care, it also presents significant challenges for clinicians who must efficiently navigate and extract relevant data from complex EHRs, medical reports, and research databases.
Generative AI(GenAI), a cutting-edge technology capable of producing human-like text and analysis, offers promising solutions to these challenges. This paper explores how GenAI can enhance information retrieval for clinicians, standardise medical information, and reduce errors in clinical practice.
Information retrieval in healthcare
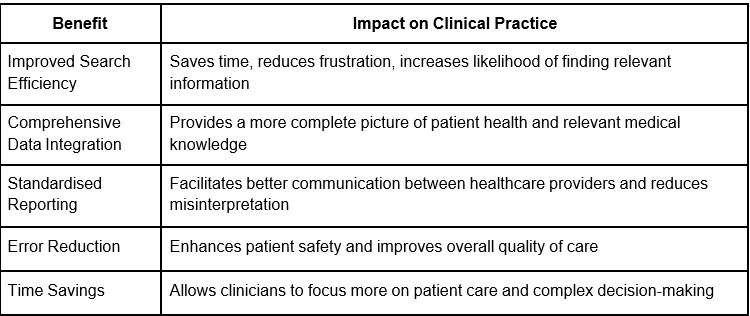
Effective information retrieval is crucial for clinicians to make informed decisions and provide high-quality patient care. GenAI systems improve this process by:
1. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
AI assistants can understand and interpret complex medical queries posed in natural language, allowing clinicians to search for information using conversational phrases rather than specific keywords or codes.
Example: An AI assistant at AIIMS could understand and interpret complex medical queries posed in Hindi or English, allowing clinicians to search for information using conversational phrases rather than specific keywords or codes.
2. Contextual understanding
These systems can analyse the context of a query within a patient's overall health profile, ensuring that retrieved information is relevant to the specific case at hand.
Example: At a rural health centre in Bhagalpur, Bihar, an AI system could analyse the context of a query within a patient's overall health profile, ensuring that retrieved information is relevant to the specific case at hand, considering factors like local disease prevalence, season, culture, food habits and available resources.
3. Multi-source integration
GenAI can simultaneously search and synthesise information from various sources, including EHRs, medical literature databases, and clinical guidelines, providing a comprehensive overview of relevant data.
Example: A GenAI system at a tertiary care hospital in Bangalore could simultaneously search and synthesise information from various sources, including the hospital's EHR system, Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) databases, and international clinical guidelines, providing a comprehensive overview of relevant data.
4. Summarisation
AI assistants can generate concise summaries of lengthy medical records or research papers, saving clinicians valuable time while ensuring they have access to critical information.
How it works:
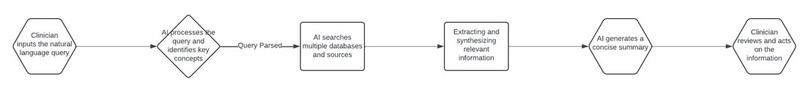
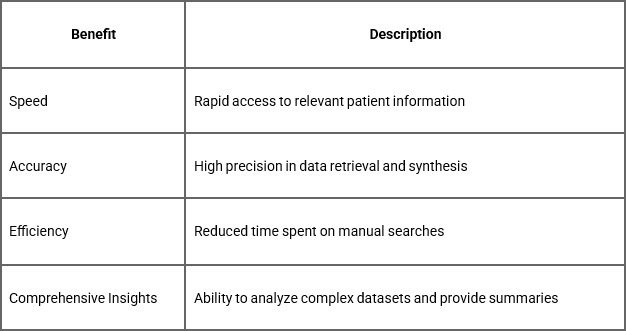
Table: Key benefits of GenAI in information retrieval
Standardisation of medical information
One of the major challenges in healthcare is the lack of standardisation in how medical information is recorded and reported. GenAI can contribute to standardisation efforts, especially in the Indian context, which encompasses multilingual and multicultural by:
A. Terminology mapping
In India, we face significant challenges due to the diversity of languages and medical practices across different states. GenAI can be crucial in mapping varied terminologies to standardised vocabularies like SNOMED CT or ICD-10.
Example: Consider a case where a patient's record from a rural clinic in Tamil Nadu describes a condition as "மாரைடMЦ" (heart attack in Tamil). The AI system can automatically map this to the standardised term "Myocardial Infarction" in English and assign the appropriate ICD-10 code (I21). This ensures that the patient's condition is understood accurately across different healthcare providers, regardless of language barriers or local terminology variations.
B. Structured data extraction
These tools can extract structured data from unstructured text, such as free-form clinical notes, and handwritten notes and organise it into standardised formats for easier analysis and comparison.
Example: A GenAI model can analyse a handwritten discharge summary from a district hospital in Uttar Pradesh. It can extract key information such as diagnosis, prescribed medications, and follow-up instructions, and organise this into a structured format compatible with electronic health record (EHR) systems. This not only improves data quality but also facilitates easier sharing of patient information between primary health centres and tertiary care hospitals.
C. Template generation
Standardised templates are essential for ensuring comprehensive and consistent medical reporting across India's diverse healthcare landscape.
Example: An AI assistant could generate a standardised template for a COVID-19 screening report, taking into account guidelines from the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR). This template would include fields for patient demographics, symptoms, travel history, comorbidities, and test results. By using such AI-generated templates, even small clinics in remote areas can ensure they're collecting all necessary information in a format that's compatible with national health databases.
D. Cross-lingual standardisation
India's linguistic diversity presents unique challenges in healthcare standardisation. GenAI can bridge these language gaps effectively.
Example: Think of a multi-state telemedicine platform connecting doctors and patients across India. A GenAI system could provide real-time translation of medical terms and concepts between languages like Hindi, Bengali, Telugu, and English. For instance, it could accurately translate and standardise descriptions of ayurvedic treatments or local herbs used in traditional medicine, ensuring that this information is correctly interpreted and recorded in the patient's medical history, regardless of the healthcare provider's linguistic background.
Standardisation flow
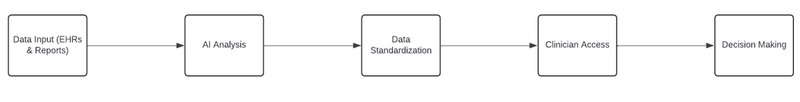
Error reduction through AI assistance
By improving information retrieval and standardisation, GenAI can significantly contribute to error reduction in clinical practice. Key areas of impact include:
- Diagnostic support
AI systems can quickly retrieve and present relevant patient history, lab results, and similar case studies, reducing the likelihood of missed or delayed diagnoses. For instance, when dealing with complex cases like tuberculosis, which is prevalent, AI can swiftly retrieve and present relevant patient history, previous X-rays, and similar case studies from the hospital's database.
- Medication management
In India where polypharmacy is common, AI tools are proving invaluable. For example, at Apollo Hospitals, AI systems flag potential drug interactions or contraindications based on a patient's comprehensive medical history. This is particularly helpful in preventing medication errors for elderly patients who often consult multiple specialists and may be on several medications.
- Clinical decision support
By providing evidence-based recommendations and alerting clinicians to potential risks or oversights, AI assistants can enhance clinical decision-making. For instance, in managing tropical diseases like dengue, which sees seasonal outbreaks in cities like Mumbai and Delhi, AI tools can alert clinicians to potential risks or oversights based on the latest treatment guidelines and local epidemiological data.
- Documentation accuracy
In many Indian hospitals, especially in tier-2 and tier-3 cities where resources are often stretched thin, GenAI can assist in creating more accurate and complete medical documentation.
Potential error reduction with AI implementation
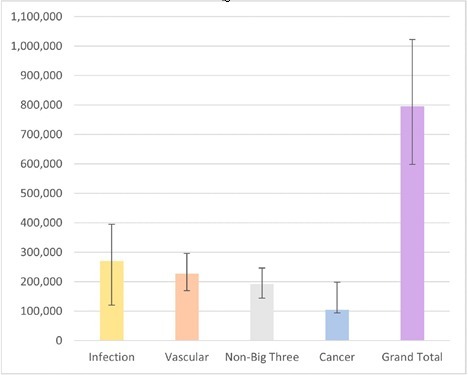
Figure 1: Annual population incidence of serious misdiagnosis-related harms from vascular events, infections, cancers and all non-Big Three others The estimated total annual US incidence for serious harms (combining "Big Three' harms with other non-"Big Three' harms) is 795 000 (probabilistic plausible range (PPR) 598000-1023000) Whiskers denote PPRs from the Monte Carlo analysis
Key benefits
Conclusion
Imagine having a smart, tireless assistant who helps you navigate patient records, research, and clinical decisions in seconds and your local language. That's what GenAI could bring to our hospitals and clinics. It instantly provides relevant info, saving you time and helping you make informed decisions.
Of course, we'll need to ensure patient privacy and train these systems on data that represents our unique population. But imagine how this could transform healthcare delivery across India, from busy urban centres to remote villages. Good days to come.
Disclaimer- The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of M3 India.
About the author of this article: Mr Rohit Kumar has done a Master's from IIT Kharagpur and is a Co-Founder of Rapida.AI also Founder and CEO of Neeba Health, Bengaluru, Karnataka.
-
Exclusive Write-ups & Webinars by KOLs
-
Daily Quiz by specialty
-
Paid Market Research Surveys
-
Case discussions, News & Journals' summaries