Medical abortion: Stepwise guide & post-procedure care- Dr. Kiran Kurtkoti
M3 India Newsdesk May 06, 2021
Medical abortion is the most effective method of terminating a pregnancy, provided the prescribed medication is administered in the right amount and at the right time. The whole process of abortion consists of various considerations- pharmacological and medico-legal, which also plays a vital role. In this first part of our new series with Dr Kiran Kurtkoti, we cover the clinical aspects of medical abortions- pharmacological management and post-abortion care.
Medical abortions- a boon to womanhood
There has always been a traditional demand for non-surgical methods of induced abortion. In a study of 495 women seeking MVA in rural Rajasthan, 32% admitted to having earlier used medical remedies such as tablets (65%), decoctions (33%) and injections (8%). [1] Following the US FDA approval on October 2001, medical abortion using mifepristone was approved by the Drug Controller of India on February 13, 2002 (Drug Controller of India, 2002). [2]
Mifepristone - Pharmacology
Mechanism of action: A derivative of norethindrone, Mifepristone, binds to the progesterone receptor with an affinity greater than that of progesterone itself, without activating the receptor, hence acting as an antiprogestin.
Effects on uterus and cervix during early pregnancy:
- It alters the endometrium by affecting the capillary endothelial cells of the decidua, resulting in separation of the trophoblast from the decidua, resulting in separation of trophoblast from the deciduas, with a resultant decrease in HCG and bleeding. This results in increased PG release.
- It softens the cervix and facilitates expulsion.
Combination of Mifepristone and Misoprostol
Numerous studies have the efficacy of various regimes of mifepristone and misoprostol or intravaginal gemeprost in the termination of early pregnancy up to 49 days duration:
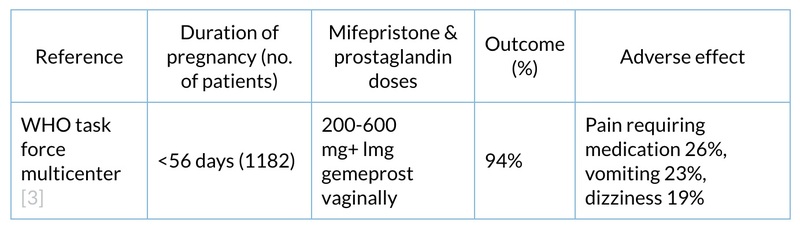
Indication and usage
- Mifepristone is indicated for the medical termination of pregnancy through 49 days pregnancy, in India.
- The duration of pregnancy may be determined from menstrual history and clinical examination.
- Ultrasound should be done if the duration of pregnancy is uncertain or if ectopic pregnancy is suspected.
- IUCD should be removed before treatment.
Contraindications
- Confirmed or suspected ectopic pregnancy/undiagnosed adnexal mass
- Chronic adrenal failure
- Concurrent, long-term steroid therapy
- History of allergy to other prostaglandins
- Haemorrhagic disorders or concurrent anticoagulant therapy
- Inherited porphyrias
The treatment is contraindicated if a patient does not have an access to medical facilities equipped to provide emergency treatment of incomplete abortions.
Role of imaging science in medical abortions
It is important to stress here that by no means should it be considered that the procedure of an MTP is deficient if USG is not done.
Pre-abortion: How can an ultrasound help?
- Documentation of pregnancy- When there is a doubt about its presence.
- Date of pregnancy- When the patient is not sure of her dates or the clinical examination does not correspond to the period cycle history.
- Confirming the diagnosis of multifetal pregnancy.
- Localisation of co-existing IUCD.
- Diagnosis of co-existing mass ultrasound can confirm co-existing fibroid, its size and location.
- Diagnosis of congenital uterine anomalies.
- Diagnosis of abnormal pregnancy, ectopic pregnancy, vesicular mole and missed abortion.
Post-abortal ultrasound
Incomplete evacuation: This is really the major concern for the provider after a medical MTP. An endometrial echo of more than 15 mm should raise a suspicion of incomplete abortion. However, in the absence of symptoms, this need not be considered. One can see hyperechogenic shadows inside the uterine cavity with the collection of fluid (bleeding) as a hypoechoic area. But, when a medical abortion has been performed, this finding should be interpreted with the clinical situation as the backdrop.
Warnings
Vaginal bleeding occurs for an average of 6-14 days. In some cases, excessive bleeding may require treatment by curettage, administration of saline infusions and/or blood transfusion. Since heavy bleeding requiring curettage may occur in about 1% of patients, special care should be taken to avoid giving this form of treatment to patients with severe anaemia Hb <8 g%. Definition of severe bleeding is using more than 2 pads per hour continuously for 2 hours.
Information for the patient
- The necessity of completing the treatment schedule including the follow-up visit approximately 14 days after taking mifepristone
- Vaginal bleeding and uterine cramping may probably occur
- Prolonged or heavy bleeding is no proof of complete expulsion
- If the treatment fails there is a risk of foetal malformation
- Patients in whom medical abortion fails will be managed by surgical evacuation
- Patients should have a telephone number that they can call in case of an emergency
Dosage and administration
WHO recommendation [4]
Day 1:
- Mifepristone administration
- The patient should read the medication guide and sign the MTP consent form
- The patient should take one 200 mg tablet of mifepristone orally
The minimum recommended interval between mifepristone & misoprostol is 24 hours.
1 to 2 days later:
- Misoprostol administration
- 4 tablets of 200 mcg (total 800 mcg) of misoprostol vaginal, sublingual, buccal route
- Anti-emetic (domperidone) and/or pain medication (dicyclomine) if necessary
- An emergency contact number is given
Day 14:
- Post-treatment examination
- Confirm abortion; no further treatment required
- If still pregnant, surgical treatment should be recommended
Drug interactions
Drugs like ketoconazole, itraconazole, erythromycin and grape juice may inhibit the metabolism of mifepristone. Drugs like rifampicin, dexamethasone and certain anticonvulsants (phenytoin, phenobarbitone, carbamazepine) may induce mifepristone metabolism (lowering the serum levels of mifepristone).
Nursing mothers
Misoprostol is converted into misoprostol acid. This is secreted in breast milk and causes diarrhoea in the infant. Hence, it is recommended that nursing mothers should feed the baby just prior to the dose of misoprostol and avoid feeding for the next 4 hours.
Adverse reactions
- Abdominal pain (cramping)
- Uterine cramping
- Nausea
- Headache
- Vomiting
- Diarrhoea
- Back pain
- Fever
- Decrease in haemoglobin <2 g/dl
Post-abortion care
Infection prevention and control: The role of prophylactic antibiotics in reducing the incidence of post-abortal infection as well as preventing long-term sequelae has been a subject of debate. Routine use of antibiotics is not recommended in medication abortion. However, if the patient has a pelvic infection, antibiotics are preferable.
Follow up visits
For medical methods of abortion, women should report after 15 days for confirmation of the completeness of abortion. Besides, follow-up visits provide an opportunity for providers to have proper counselling on contraception, hygiene and other medical ailments.
Post-abortion contraception

Click here to see references
Disclaimer- The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author's and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of M3 India.
Dr Kiran Kurtkoti is a practising Obstetrician & Gynecologist with an experience of 28 years.
-
Exclusive Write-ups & Webinars by KOLs
-
Daily Quiz by specialty
-
Paid Market Research Surveys
-
Case discussions, News & Journals' summaries