Indicators of outcome are identified for nivolumab treatment of patients with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma
ESMO Virtual Congress 2020 Sep 22, 2020
The predictive value provided by T effector (Teff) and angiogenesis (Angio) signatures was augmented by Kidney Immune Classification (KIC) of tumour microenvironments, which were also indicative of outcome following nivolumab treatment of patients with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). These findings were presented by Maxime Meylan of the Inflammation, complement and cancer, Centre de Recherche des Cordeliers in Paris, France at the ESMO Virtual Congress 2020.
Meylan and colleagues were prompted by a report from the NIVOREN GETUG-AFU 26 study that nivolumab provided safety and efficacy for patients with metastatic ccRCC in a real world setting to undertake this Kidney Immune Classification (KIC) project. Their study determined gene expression signatures and tumour microenvironments to assess their association with patient outcome following nivolumab with the aim of identifying biomarkers for nivolumab activity.
The translational cohort of Nivoren comprised 324 ccRCC FFPE samples; of these 184 were profiled by 3’ RNA sequencing and split in a Discovery (n=79) and Validation (n=105) cohorts.
Using the procedure outlined in the IMmotion 150 RCC study, the investigators assessed the impact of Teff and Angio signatures on patient outcome, based on median mRNA expression values. Their next step was to perform an unsupervised analysis using the Microenvironment Cell Populations- (MCP-) Counter to classify tumours according to their infiltration by 8 immune (I; fibroblasts) and 2 stromal (S; endothelial) cell populations, with the aim of characterising the tumour microenvironment.
The study outcomes included response rate (RR; best response determined by complete or partial response) and PFS.
KIC defined tumour microenvironments that were linked to patient outcomes after nivolumab treatment
Although the Angio and Teff signatures taken separately were not predictive of outcomes following nivolumab, the combination of these two signatures was highly informative.
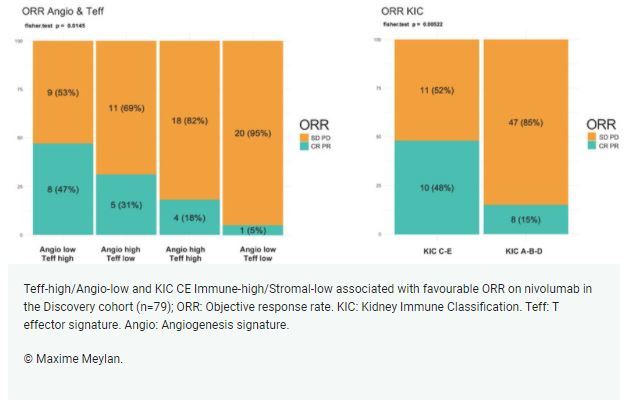
Combined Angio and Teff signatures applied together in the analysis revealed that the most aggressive tumours, Teff-high/Angio-low and Teff-low/Angio-low, were significantly associated with RR and PFS in the Discovery cohort. Favourable outcome was indicated by a Teff-high/Angio-low signature, which associated with a RR of 47% (p = 0.01) and median PFS of 10.1 months (95% confidence interval [CI] 2.7- not estimable [NE]; p = 0.0005), whereas Teff-low/Angio-low associated with poorer RR of 5% (p = 0.01) and median PFS of just 2.6 months (95% CI 2.1-2.8; p = 0.0005).
Unsupervised classification identified 5 KIC subtypes, which were designated A to E. KIC C+E tumours had high levels of CD8+ cells, but low numbers of stromal cells (CD8-high/S-low) and were associated with Improved RR and PFS, as compared to KIC A tumours (I-low/S-low), KIC B (I-low/S-high), and KIC C tumours (I-high/S-high).
Evaluation of the KIC classification identified tumour microenvironments that were associated with nivolumab outcomes in the Discovery cohort. Specifically, KIC C-E associated with a 48% RR (p = 0.005) and median PFS of 11.4 months (95% CI 2.4-NE; p = 0.03) and KIC A-B-D- associated with a 15% RR (p = 0.005) and median PFS of just 2.8 months (95% CI, 2.7-4.2; p = 0.03). In the Validation cohort, the KIC classification was also associated with nivolumab outcome, the KIC C-E displayed 36% RR (p = 0.0438) and the KIC A-B-D 11% RR (p = 0.0438).
According to principal component analysis, a similar contribution of KIC stromal cells and the Angio signatures was apparent in tumours associated with the worst outcomes.
Conclusions
The authors stated that this is the first report from a prospective trial that Immune high/angiogenesis and stromal low signatures may be predictive of nivolumab efficacy in patients metastatic ccRCC patients.
Their findings further suggest that KIC provides a first step in unravelling the deleterious clinical impact of potential immunosuppression that is contributed by neutrophils, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells in the tumour microenvironment.
Funding was reported from the Institut National du Cancer and Bristol-Myers Squibb.
This article is a news release from ESMO 2020 Press Meeting. Read the original here.
-
Exclusive Write-ups & Webinars by KOLs
-
Daily Quiz by specialty
-
Paid Market Research Surveys
-
Case discussions, News & Journals' summaries