SGLT2 Inhibitors in Heart Failure: Clinical Case Scenarios
M3 India Newsdesk Apr 18, 2024
This article explains the role of SGLT2 in treating heart failure, its dosages and possible side effects. It also includes questions related to the case study that is discussed in this article.
SGLT2 inhibitors in the treatment of heart failure
Below are the points to consider while using SGLT2 inhibitors in the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction:
- Identify suitable patients to start using SGLT2 inhibitors.
- Examine obstacles to the start of SGLT2.
- Create a plan to implement and oversee SGLT2 in a patient with HFrEF.
- Identify SGLT2 inhibitors that heart failure patients may take.
- List the essential laboratory parameters to evaluate before starting an SGLT2 inhibitor.
- Carry out a strategy to overcome SGLT2 inhibitor pricing obstacles.
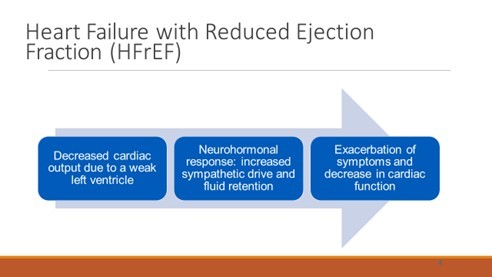
Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction( HFrEF)
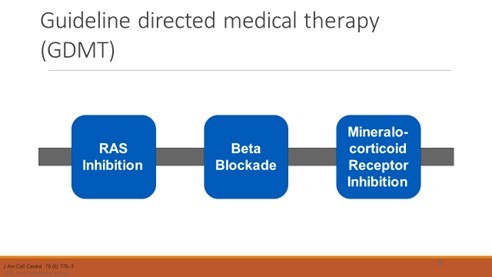
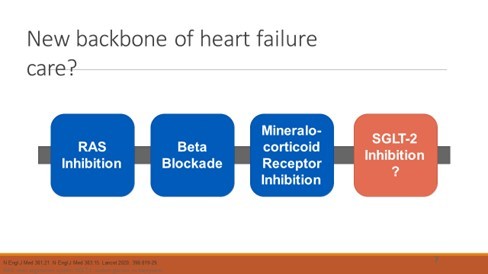
Guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT)
The case
A 63-year-old female with a history of coronary artery disease (CAD), heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), and anxiety. She presents to her primary care physician's (PCP) office for her annual visit.
| Home medications | Vitals and pertinent labs |
|
Aspirin 75 mg daily |
Blood pressure (BP): 112/72 mm Hg |
|
Atorvastatin 80 mg daily |
HR: 74 beats per minute (bpm) |
|
Metoprolol succinate 50 mg daily |
eGFR: 50 mL/min/1.73 m2 |
|
Cardace 10 mg daily |
Serum creatinine: 1.4 mg/dL(baseline 1.5) |
|
Spironolactone 25 mg daily |
Sodium: 136 mEq/L |
|
Furosemide 40 mg daily |
Potassium: 4.2 mEq/L |
|
Sertraline 50 mg daily |
-
Exclusive Write-ups & Webinars by KOLs
-
Daily Quiz by specialty
-
Paid Market Research Surveys
-
Case discussions, News & Journals' summaries