Emerging Therapies in Type 2 Diabetes
M3 India Newsdesk Nov 08, 2023
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterised by elevated blood sugar levels due to insulin resistance & inadequate insulin production. This article explores innovative treatments & technologies transforming type 2 diabetes management, offering the potential for improved patient care.
Several factors limit the ability to normalise blood sugar in diabetic patients. These include:
- The failure to specifically address every pathophysiological problem linked to hyperglycemia.
- Side effects of medication
- Contraindications to use of selected medications (e.g., renal dysfunction, heart failure)
- Risks for hypoglycemia
- The widespread correlation between rigorous glycemic management and an increased risk of weight gain
In this article, we will explore some of the emerging therapies that are revolutionising the way we manage type 2 diabetes.
1. Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
- With the advent of Glycemic variability ( GV ), Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) technology has made significant strides in recent years, offering patients with type 2 diabetes real-time data about their glucose levels.
- CGM systems involve a small sensor placed under the skin to monitor glucose levels continuously. This data can be wirelessly transmitted to a smartphone or insulin pump, giving users immediate feedback on their blood sugar levels.
- The ability to track glucose trends throughout the day allows for better control and management of diabetes. It also helps prevent hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) episodes.
- With CGM, patients and healthcare providers can make more informed decisions regarding medication adjustments and lifestyle changes.
2. GLP-RAs and SGLT2 inhibitors
In the past decade, seven cardiovascular outcome trials have provided consistent data in reducing cardiovascular events in people with T2D.
For SGLT2 inhibitors
- CREDENCE
- EMPA-REG
- CANVAS
- DECLARE-TIMI
For GLP1- RAs
- ELIXA
- SUSTAIN-6 for GLP1- RAs
- LEADER for GLP1- RAs
Metaanalyses of the cardiovascular outcomes trials show that some GLP-1 RAs can reduce major cardiovascular events, cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction rates, and stroke, among other benefits. For these reasons, the ADA, the EASD and the European Society of Cardiology published recommendations for the prescription of GLP-1 RAs and SGLT2 inhibitors with proven cardiovascular or renal benefits to patients with T2D and established CVD or high cardiovascular risk.
The choice to treat with these medications as first-line monotherapy in patients with atherosclerotic CVD or high cardiovascular risk should be made without regard to the patient's individualised HbA1c target or baseline HbA1c. Also, a significant advantage of GLP-1 RA and SGLT2 inhibitor treatments is their effect on body weight.
Furthermore, recent studies have shown that GLP-1 RAs and SGLT2 inhibitors could have the potential for treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, two conditions with currently very limited therapeutic options. Nevertheless, there are currently no randomised clinical trials that provide solid proof in favour of this use case.
Although GLP-1 RAs and SGLT2 inhibitors are generally well tolerated, the long-term safety of these drugs (> 10 years) has not been evaluated.
3. Tirzepatide
Tirzepatide is a novel once-weekly injectable single-peptide molecule with glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide(GIP) and GLP-1 RA activity. The combined action at both receptors may act synergistically, providing additional effects on glycaemic control and body weight reduction.
- In the SURPASS-1 to -5 clinical trials, the efficacy of tirzepatide in people with T2D was investigated which showed
- Robust
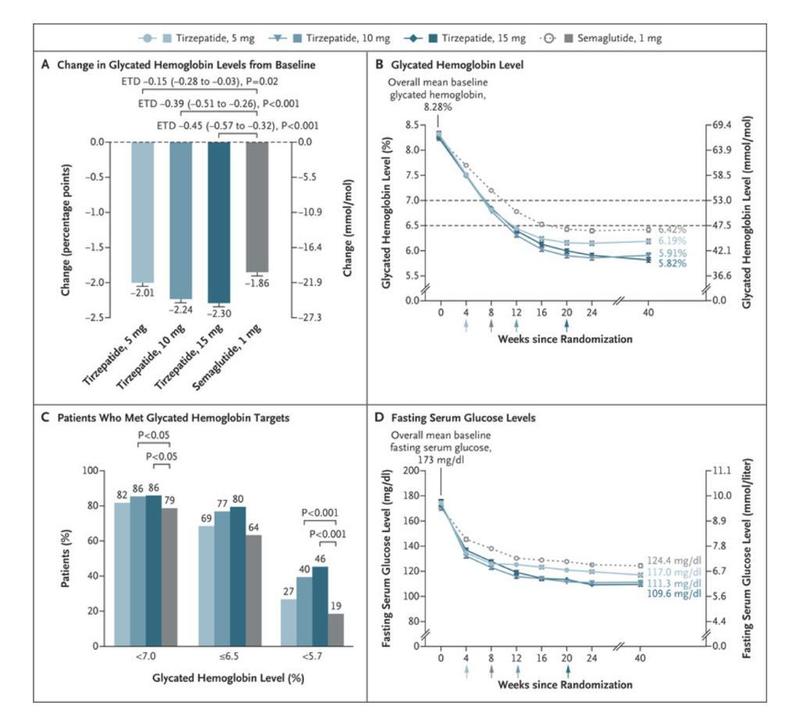
- Dose-dependent reductions in HbA1c levels (− 2.30% with the 15 mg dose after 40 weeks of treatment compared with −1.86% with semaglutide 1 mg
- Significant drops in body weight (− 12.4 kg with the 15 mg dose versus − 6.2 kg with the 1 mg semaglutide dose)
- In a substudy of SURPASS-3 in patients with continuous glucose monitoring, those receiving tirzepatide had a greater proportion of time in the tight target range (71–140 mg/dl) than those receiving insulin degludec.
- In these trials up to 69% of patients achieved a more ambitious goal of ≥ 10% weight loss, and up to 43% experienced weight loss of ≥ 15%. he majority of the body weight drop was caused by less fat mass.
- In comparison to those receiving a placebo, semaglutide 1 mg, or basal insulin, a significant proportion of participants treated with tirzepatide (all doses) achieved the triple objective of an HbA1c<5.7% with ≥ 5% weight loss and without hypoglycemia, according to a recent post hoc analysis of the SURPASS-1 to -5 trials.
- Tirzepatide (all doses) was also associated with clinically significant reductions in blood pressure and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Furthermore, tirzepatide (10 mg and 15 mg) was associated with a significant reduction in liver fat content and visceral and abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue volumes compared with insulin degludec in a subpopulation of the SURPASS-3 study.
- Tirzepatide presented a safety profile similar to that of GLP-1 RAs, mainly consisting of mild-to-moderate gastrointestinal events and no increased risk of hypoglycaemia.
- GLP-1 RAs decelerate gastric emptying, curb postmeal glycaemic increments, and reduce appetite, energy intake, and body weight. Although tirzepatide is associated with the improvement of several cardiovascular risk factors (e.g., blood pressure, lipid profile, abdominal circumference), the long-term study of cardiovascular outcomes is still underway.
- The SURPASS-CVOT trial (NCT04255433) is currently investigating the efficacy and safety of tirzepatide compared with the GLP-1 RA dulaglutide in preventing major cardiovascular events.
- Tirzepatide was included in the recent ADAEASD consensus as a drug with very high efficacy in achieving glycaemic targets and high potential in weight reduction. In 2022, tirzepatide was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration and by the European Medicines Agency for the treatment of T2D and is currently in development for chronic weight management.
4. Glucokinase activators ( GKA’s)
- Dorzagliatin is an orally bioavailable, dual-acting GKA that stimulates pancreatic and hepatic glucokinase in a glucose-dependent manner to improve glycemic control in patients with T2D.
- Dorzagliatin showed promise in increasing the pancreatic number of cells that secrete insulin.
- Multiple phase 1 trials and one phase 2 trial of dorzagliatin have been completed in China and the United States.
- In addition to effectively reducing 24-h plasma glucose levels, dorzagliatin improved the GSIS (Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion) in patients with T2D who were treated for 28 days, as indicated by a significant increase in the early-phase insulin secretion index and homeostasis model assessment 2 of beta-cell function (HOMA2-β) from baseline in a phase 1 trial.
- Phase 2 trials showed significant improvement in the glucose disposition index and reductions in insulin resistance indicated by homeostasis model assessment 2 of insulin resistance (HOMA2-IR. In order to assess the effectiveness and long-term safety of dorzagliatin, drug-naïve patients with T2D participated in the phase 3 placebo-controlled SEED research, which included a 24-week double-blind treatment period and a subsequent 28-week open-label period.
Conclusion
- The landscape of type 2 diabetes management is continually evolving.
- Additionally, the development of an artificial pancreas and the integration of telemedicine and digital health solutions are making diabetes management more accessible and convenient for patients.
- As we move forward, the focus will be on integrating these emerging therapies and technologies into comprehensive treatment plans, emphasising personalised medicine, and empowering patients to actively participate in their own care.
- With these advancements, there is hope for better diabetes management and an improved quality of life for those living with type 2 diabetes.
Disclaimer- The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of M3 India.
About the author of this article: Dr. Vigneshwaran Rajendran, a Fellow in Diabetology and Endocrinology, currently works as a Consultant Diabetologist at Frontier Lifeline Hospital, Chennai, Tamil Nadu (Unit of Dr. K. M. Cherian Heart Foundation).
-
Exclusive Write-ups & Webinars by KOLs
-
Daily Quiz by specialty
-
Paid Market Research Surveys
-
Case discussions, News & Journals' summaries