Chemotherapy Regimens in Lung Cancer
M3 India Newsdesk Nov 23, 2023
This article provides detailed case studies illustrating the multidisciplinary management of lung cancer, emphasising the role of surgery, radiation, and various chemotherapy regimens based on the type and stage of the disease.
CASE-1
A 48-year-old female, presented with right-sided chest pain.
- CECT thorax was done which showed a mass lesion in the posterior segment of the right upper lobe (Figure 1).
- CT-guided biopsy of the lung mass showed features of adenocarcinoma.
- A PET CT scan was done and it showed FDG avid right upper lobe lung mass with the absence of distant metastatic disease.
- Molecular studies (RT-PCR) showed EGFR deletion 19 mutation.
The case was discussed in the tumour board and she underwent right upper lobectomy + mediastinal lymph node dissection and the final stage was pT3N0, margins negative, node-negative.
She received 4 cycles of adjuvant chemotherapy with Cisplatin + Pemetrexed followed by one year of targeted therapy with Osimertinib. She is healthy after 5 years of treatment.
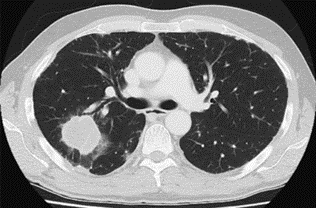
Figure-1 Mass lesion in the posterior segment of the right upper lobe
CASE-2
A 60-year-old male, smoker, presented with cough and breathlessness.
- CECT thorax showed right upper lobe lung mass and bulky mediastinal nodes (Figure 2).
- CT-guided biopsy of lung mass showed features of squamous cell carcinoma.
- A PET CT scan was done and no evidence of distant metastatic disease was found.
- Contrast-enhanced MRI brain was normal.
The case was analysed in tumour board and he was treated with Concurrent chemoradiation with weekly Paclitaxel + Carboplatin followed by one year of adjuvant immunotherapy with Durvalumab.
He is doing well after the completion of 3 years of his treatment.
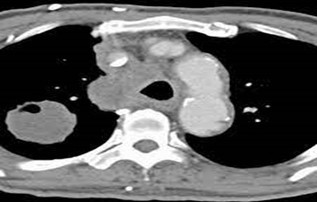
Figure 2- Right upper lobe lung mass with bulky mediastinal nodes
Case 1 had Stage IIB disease and case 2 had Stage IIIB disease. It is clear that the management of lung cancer involves a multidisciplinary approach including surgery, radiation and systemic therapy (chemotherapy, targeted therapy and immunotherapy) and depends upon the type and stage of lung cancer.
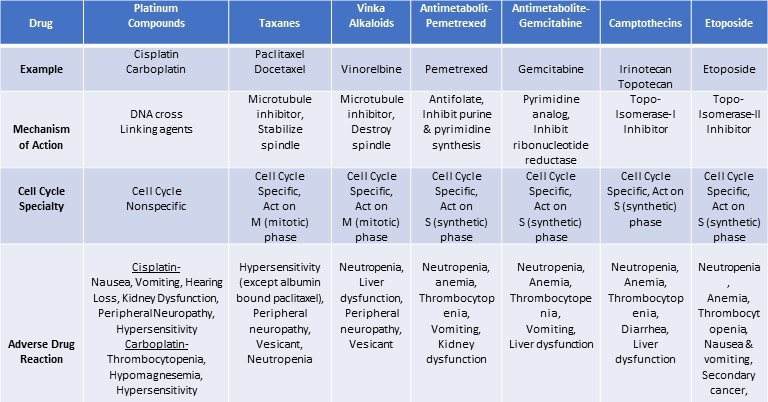
Chemotherapy regimens in lung cancer
A. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
- Almost 85% of lung cancers are non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC). The main histological subtypes are adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and large cell carcinoma.
- Platinum is the most commonly used chemotherapeutic agent and platinum-based doublet chemotherapy is the standard of care first-line therapy for most patients with NSCLC.
- Platinum compounds are usually combined with taxanes, vinka alkaloids, antimetabolites, camptothecins or etoposide. Pemetrexed, an antimetabolite, is effective only in non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer patients.
These chemotherapy regimens are used in many ways depending on the stage of cancer and other factors.
- Neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy regimens-
Adjuvant chemotherapy is chemotherapy used after primary treatment (surgery or radiation) to prevent the recurrence of the disease.
- Stage IA NSCLC patients are treated with surgery alone and there is no role of adjuvant chemotherapy for these patients if adequate.
- In Stage IB and II NSCLC, four cycles of adjuvant chemotherapy are given after upfront surgery to present recurrence and to increase overall survival.
- There is a role of adjuvant targeted therapy with Osimertinib for patients with Stage IB-IIIA disease with EGFR exon 19 deletion or exon 21 L858R mutation.
- Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is chemotherapy used before primary treatment (surgery or radiation) to treat micrometastases, to downstage the malignancy and to reduce postoperative morbidity.
- In Stage II and IIIA NSCLC patients, at least 3 cycles of neoadjuvant chemotherapy are offered before surgery.
Chemotherapy regimens used for neoadjuvant or adjuvant purposes are mentioned below.
- Cisplatin/Carboplatin + Pemetrexed 3 weekly only in non-squamous histology
- Cisplatin/Carboplatin + Gemcitabine 3 weekly
- Cisplatin + Docetaxel 3 weekly
- Cisplatin + Vinorelbine 3 weekly
- Cisplatin + Etoposide 3 weekly
- Carboplatin + Paclitaxel 3 weekly
- Concurrent chemotherapy regimens-
Concurrent chemotherapy is chemotherapy given along with radiation therapy aiming to eradicate the malignancy.
- Stage IIIA and IIIB NSCLC patients, who are not surgical candidates, are typically treated with a combination of chemotherapy and radiation.
- There is a role of adjuvant immunotherapy with Durvalumab for patients with Stage IIIA-IIIB disease treated with definite chemo-radiation.
Concurrent chemotherapy regimens are mentioned here.
- Cisplatin + Etoposide 4 weekly for two cycles
- Carboplatin + Paclitaxel weekly for six to seven cycles
- Cisplatin/Carboplatin + Pemetrexed 3 weekly for three to four cycles only in non-squamous histology
- Palliative chemotherapy regimens-
Metastatic or Stage IV NSCLC patients are evaluated for targetable or actionable mutations like EGFR, ALK, ROS-1, BRAF, RET, MET exon 14 skipping mutation and NTRK gene fusion with the help of next-generation sequencing or other molecular testing.
- If no targetable mutation is found, PD-L1 testing by immunohistochemistry plays an important role in deciding further course of action.
- If PD-L1 is equal to or more than 50%, the patient is treated with immunotherapy alone while if PD-L1 is less than 50%, chemotherapy is combined with immunotherapy.
- If the patient is symptomatic, chemotherapy is started while waiting for the results of the above-mentioned molecular testing.
First-line palliative chemotherapy regimens useful in NSCLC patients are mentioned here-
- Cisplatin/Carboplatin + Pemetrexed only in non-squamous histology
- Cisplatin/Carboplatin + Paclitaxel/ Albumin-bound-paclitaxel
- Cisplatin/Carboplatin + Docetaxel
- Cisplatin/Carboplatin + Gemcitabine
- Cisplatin/Carboplatin + Etoposide
- Gemcitabine + Docetaxel/Vinorelbine
Single-agent and combination chemotherapy regimens not previously used can be offered in second or subsequent lines to metastatic NSCLC patients.
B. Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
Almost 15% of lung cancers are small cell lung cancers (SCLC). Its prognosis is worse than NSCLC.
It is divided into two types- limited-stage disease and extensive-stage disease.
Limited-stage SCLC patients are treated with a combination of platinum-based chemotherapy and thoracic radiation with curative intent and prophylactic cranial radiation is offered to patients achieving a partial or complete response to chemoradiotherapy.
Extensive-stage SCLC patients should be treated with chemotherapy in combination with immunotherapy to increase overall survival.
First-line chemotherapy regimens used in both limited-stage and extensive-stage SCLC patients are mentioned below-
- Cisplatin/Carboplatin + Etoposide
- Cisplatin/Carboplatin + Irinotecan
Topotecan, paclitaxel, docetaxel, temozolomide, gemcitabine and many other chemotherapeutic agents are used in second or subsequent line for extensive-stage SCLC patients progressing on first-line treatment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the management of lung cancer involves a multidisciplinary approach. With the advent of targeted therapy and immunotherapy, the survival of these patients has improved significantly but chemotherapy remained the backbone of treatment and is used in all types and stages of lung cancer in one way or another to increase the survival of these patients.
Disclaimer- The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of M3 India.
About the author of this article: Dr. Mohit Saxena is a Medical Oncologist from Gurgaon.
-
Exclusive Write-ups & Webinars by KOLs
-
Daily Quiz by specialty
-
Paid Market Research Surveys
-
Case discussions, News & Journals' summaries