CA Channel Blockers Used in HTN
M3 India Newsdesk Apr 04, 2024
The article delineates the classification, characteristics, & uses of calcium channel blockers (CCBs), highlighting their diverse therapeutic applications & potential adverse effects. It also introduces novel CCBs, discussing their distinct pharmacological properties and clinical implications.
Key takeaways
- Calcium channel blockers (CCBs) are medications that treat high blood pressure and other heart-related health conditions.
- Common CCB side effects include constipation, swelling in the arms and legs, and a slow heart rate. Fatigue, flushing, and dizziness can also occur.
- CCBs can cause worsening of heart problems, such as heart failure. These medications are usually avoided in people with heart failure.
Calcium Channel Blockers (CCBs)
CCBs are medications that are used widely to control blood pressure and manage symptoms of angina. As a class, they are well tolerated and are associated with few side effects.CCBs are classified as DHPs and Non-DHPs.
The characteristics features are as follows;
- DHP CCBs are in four generations.
- They are vascular-selective and potent vasodilators.
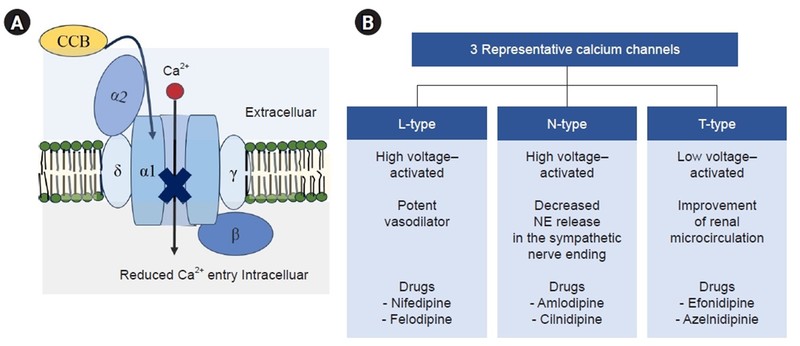
- They block L-type calcium channels mainly but the novel ones block N-type and T-type channels leading to organ protective effects.
- They have potent BP-lowering effects and suppress atherosclerosis and coronary vasospasm.
- They reduce LVH and arterial stiffness.
- Combined with RAAS blockers, they cause reduced proteinuria and improved kidney function.
- They are indicated in hypertension in elderly patients, ISH, angina pectoris and coronary vasospasm.
DHPs
Act on vascular smooth muscles, promoting vasodilation without significantly affecting cardiac function.
- First-generation nifedipine, nicardipine (rapid onset and short duration of vasodilatation).
- Second-generation extended-release nifedipine, felodipine, (slow release and short duration).
- Third-generation amlodipine and azelnidipine (slow onset and long duration, high vascular selectivity and less sympathoexcitation).
- Fourth-generation lacidipine, lercanidipine and cilnidipine ( strong lipophilic, stable, reduced peripheral oedema and broad therapeutic spectrum).
NON-DHPs
- They Block L-type calcium channels in the heart and hence can be used in PSVT.
- They should be carefully used for heart block, bradycardia and constipation.
- First generation : Verapamil and Diltiazem
- Second-generation Verapamil SR and Diltiazem SR
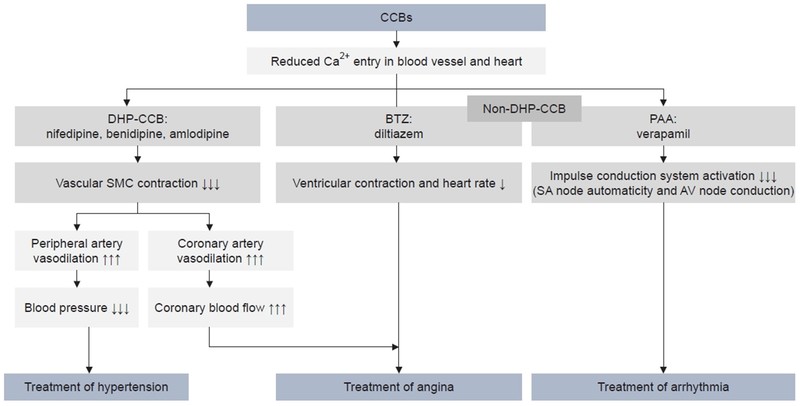
The above diagram shows the administration of various DHP CCBs in various conditions
The above diagram shows the indications based on the mechanism of action.
Indications
Verapamil
- PSVT and to control ventricular rate
- As monotherapy in angina
- Rarely in HTN as it causes cardio-depression
Diltiazem
- Angina especially vasospastic angina
- Hypertension
DHP CCB
Medical conditions treated or associated with calcium channel-blocking agents:
- Angina
- Angina pectoris prophylaxis
- coronary artery disease without heart failure
- Headache
- High Blood Pressure
- Hypertensive emergency
- Migraine
- Raynaud's syndrome
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Off‐label uses for CCBs
CCBs have been studied in many other diseases. They may be beneficial in conditions involving peripheral vasospasm (Raynaud’s phenomenon, migraine and cluster headaches, high‐altitude pulmonary oedema, and even premature labour).
Hypertension associated with cyclosporine, nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs, or widened pulse pressure is often improved by CCBs
ADR
DHP tachycardia, palpitations, oedema flushing headache. The most important clinical points are as follows;
- Despite having an intrinsic diuretic effect, the dihydropyridines cause peripheral oedema. The oedema represents a redistribution of extracellular fluid rather than a net retention of salt and water and hence does not respond to diuretics.
- Short-acting Nifedipine was associated with myocardial ischaemia and mortality due to rebound activation of sympathetic activity caused by its short duration and rapid onset of vasodilating activity.
- On the other hand, diltiazem has actions on the myocardium and conduction system particularly on the AV node, It causes strong coronary vasodilation, hence used in vasospastic Angina.
Novel CCB
Clevidipine
- Clevidipine is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker indicated for the reduction of blood pressure when oral therapy is not feasible or desirable.
- Clevidipine is used IV only.
- It has a half-life of approximately one minute. It is rapidly inactivated by esterases, hence indicated in hypertensive emergencies.
Azelnidipine
- Azelnidipine is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker.
- Azelnidipine is an L and T calcium channel blocker. Unlike nicardipine, it has a gradual onset and has a long-lasting antihypertensive effect, with little increase in heart rate.
- Azelnidipine delays the progression of urinary albumin excretion and carotid atherosclerosis, which was not observed with amlodipine.
Disclaimer- The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of M3 India.
About the author of this article: Dr Padma Lakshminarayana is a professor and HOD of pharmacology at Sapthagiri Institute of Medical Sciences and Research Centre in Bengaluru.
-
Exclusive Write-ups & Webinars by KOLs
-
Daily Quiz by specialty
-
Paid Market Research Surveys
-
Case discussions, News & Journals' summaries