Avulsed Teeth: An Insight Into Storage Media
M3 India Newsdesk Jun 04, 2024
A dental avulsion is defined as the total removal of a tooth from its alveolar bone socket. This article gives a brief idea of various storage media options available and their effectiveness in maintaining the viability of avulsed teeth.
Introduction
Dental trauma is one of the most critical oral injuries that occur at any age. Dental emergencies can be distressing, especially when they involve the avulsion (complete displacement or knocked out) of a tooth due to trauma. The longer the tooth remains out of its socket, the lower the likelihood of successful re-implantation. Ideally, the tooth should be reinserted within 30 minutes of the avulsion to maximise the chances of success.
The viability of the periodontal ligament (PDL) cells that remain on the root surface, the integrity of the root cementum, and the absence of bacterial contamination are factors that directly relate to the extra-alveolar period, the type of storage after avulsion, and changes to the root surface.
These factors determine the prognosis of a replanted tooth and its maintenance on the dental arch for the longest possible time. The selection of storage media for holding the extracted tooth until a dentist can replace it is essential for improving the prognosis of such teeth.
Criteria for ideal storage media
- Maintains cell viability: The storage medium should support the survival of periodontal ligament (PDL) cells, which are crucial for successful re-implantation.
- pH balance: A neutral or slightly alkaline pH is preferred to maintain cellular integrity.
- Osmolarity: The osmolarity of the storage medium should be similar to that of the body's fluids to prevent cellular damage.
- Antimicrobial properties: The storage medium should have antimicrobial properties to minimise the risk of infection.
- Availability and accessibility: The storage medium should be readily available and easy to access in emergencies.
Steps for proper preservation
- Act quickly
- Handle the tooth carefully: Avoid touching the root surface of the avulsed tooth to prevent damage to the delicate PDL cells.
- Clean the tooth gently: Rinse the tooth briefly under running water to remove dirt or debris. Avoid scrubbing the tooth or using any cleaning products.
- Choose a suitable storage medium: Place the tooth in a container filled with the chosen storage medium, ensuring that it is completely submerged.
- Handling and transport: When storing an avulsed tooth, handling it with care is essential to avoid damaging the delicate PDL cells. Hold the tooth by the crown (top part) and avoid touching the root if possible. After placing the tooth in the chosen storage medium, it should be transported to the dental office as soon as possible for re-implantation.
Common storage media options
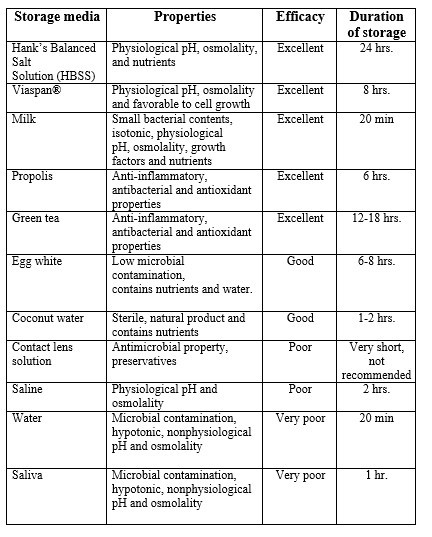
Conclusion
As of now, no single product or solution has all the necessary qualities to be recommended as the best storage medium for avulsed teeth. Taking together the characteristics, efficacy, availability and accessibility, milk appears as the best followed by HBSS as a temporary storage medium for avulsed teeth before replantation, and its use is recommended by the International Association of Dental Traumatology and the American Academy of Paediatric Dentistry.
By acting promptly and selecting an appropriate storage medium, individuals can maximise the chances of successful reimplantation and long-term retention of avulsed teeth, minimising the impact of dental trauma on oral health and overall well-being.
Disclaimer- The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of M3 India.
About the author of this article: Dr Pooja Sarda is a practising specialist in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery at Sangli, Maharashtra.
-
Exclusive Write-ups & Webinars by KOLs
-
Daily Quiz by specialty
-
Paid Market Research Surveys
-
Case discussions, News & Journals' summaries